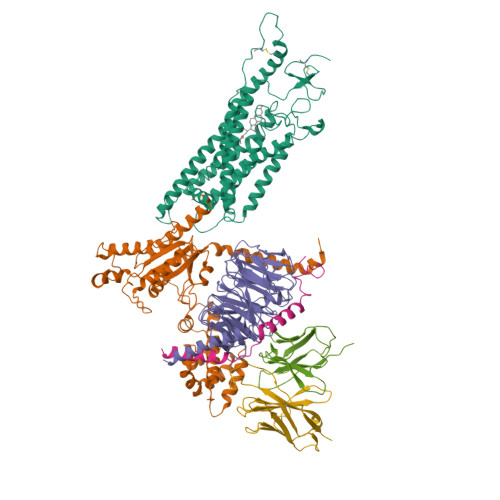
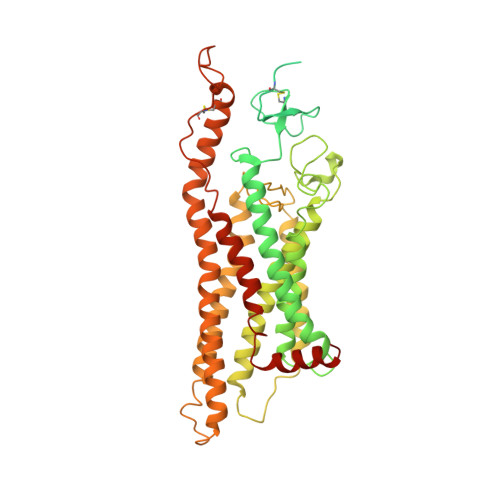
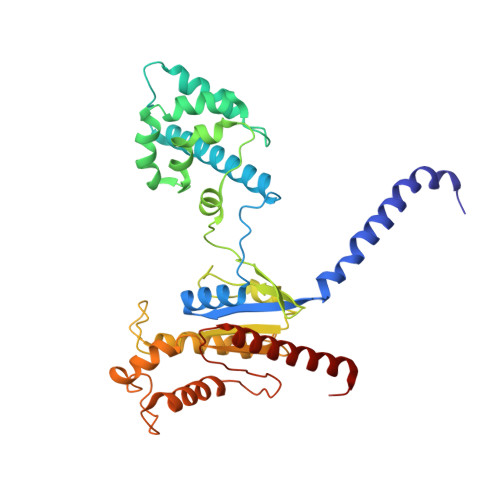
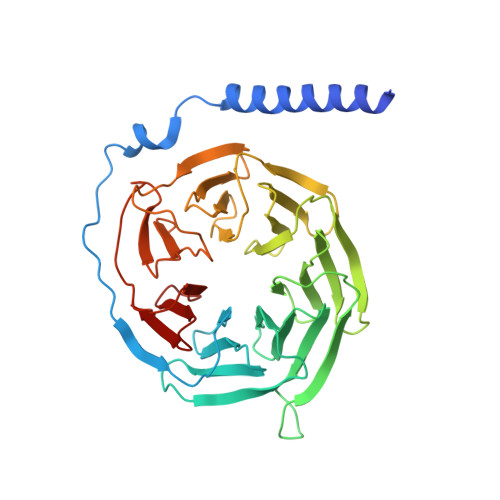
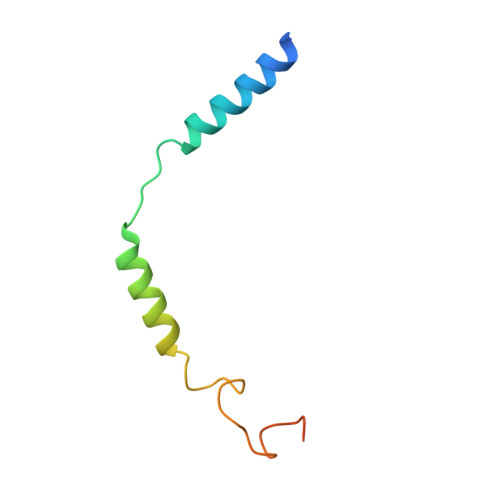
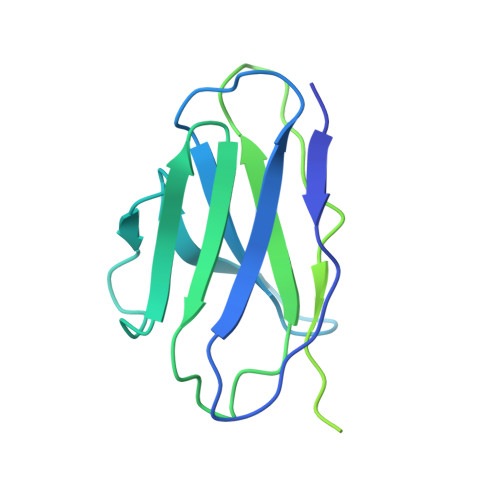
Cryo-EM structure of oxysterol-bound human Smoothened coupled to a heterotrimeric Gi.
Qi, X., Liu, H., Thompson, B., McDonald, J., Zhang, C., Li, X.(2019) Nature 571: 279-283
- PubMed: 31168089
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1286-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OT0 - PubMed Abstract:
The oncoprotein Smoothened (SMO), a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) of the Frizzled-class (class-F), transduces the Hedgehog signal from the tumour suppressor Patched-1 (PTCH1) to the glioma-associated-oncogene (GLI) transcription factors, which activates the Hedgehog signalling pathway 1,2 . It has remained unknown how PTCH1 modulates SMO, how SMO is stimulated to form a complex with heterotrimeric G proteins and whether G-protein coupling contributes to the activation of GLI proteins 3 . Here we show that 24,25-epoxycholesterol, which we identify as an endogenous ligand of PTCH1, can stimulate Hedgehog signalling in cells and can trigger G-protein signalling via human SMO in vitro. We present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of human SMO bound to 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol and coupled to a heterotrimeric G i protein. The structure reveals a ligand-binding site for 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol in the 7-transmembrane region, as well as a G i -coupled activation mechanism of human SMO. Notably, the G i protein presents a different arrangement from that of class-A GPCR-G i complexes. Our work provides molecular insights into Hedgehog signal transduction and the activation of a class-F GPCR.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.