Crystal structure and specific location of a germin-like protein with proteolytic activity from Thevetia peruviana.
Cruz, W.T., Bezerra, E.H.S., Ramos, M.V., Rocha, B.A.M., Medina, M.C., Demarco, D., Carvalho, C.P.S., Oliveira, J.S., Sousa, J.S., Souza, P.F.N., Freire, V.N., da Silva, F.M.S., Freitas, C.D.T.(2020) Plant Sci 298: 110590-110590
- PubMed: 32771148
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110590
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
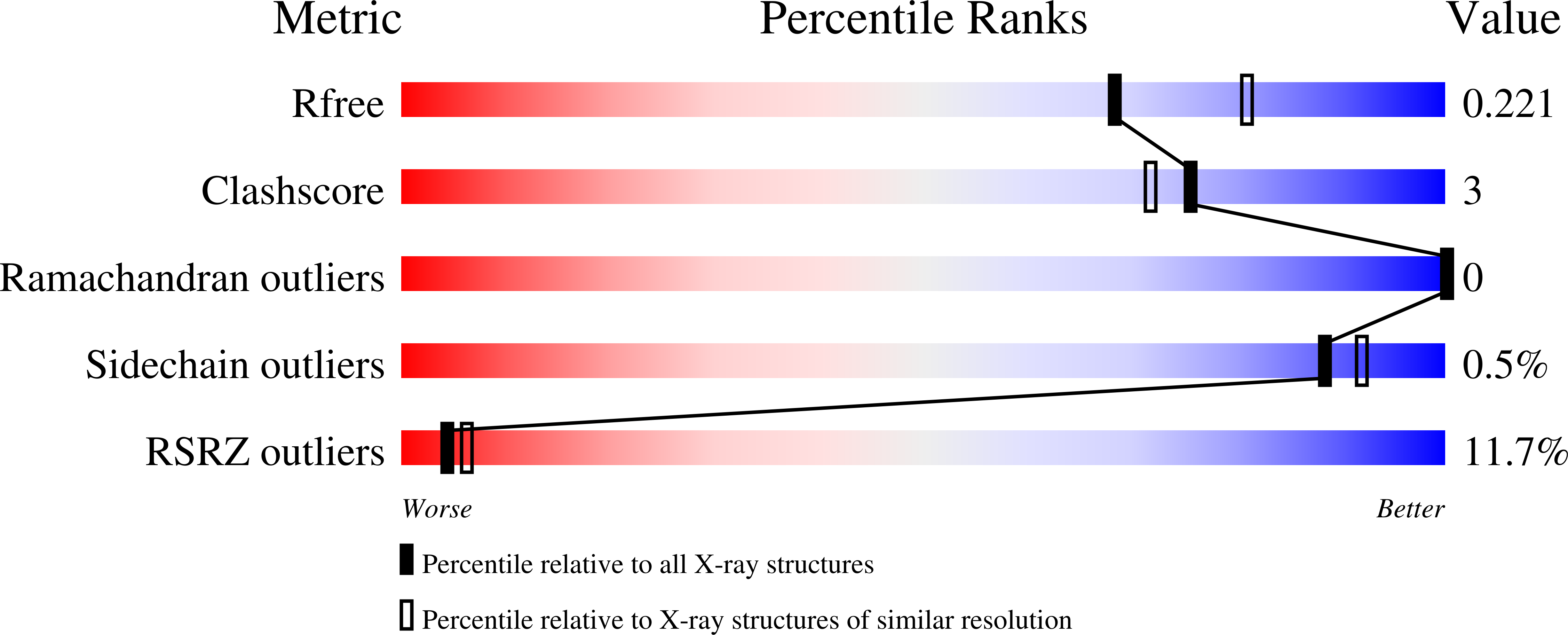
6ORM - PubMed Abstract:
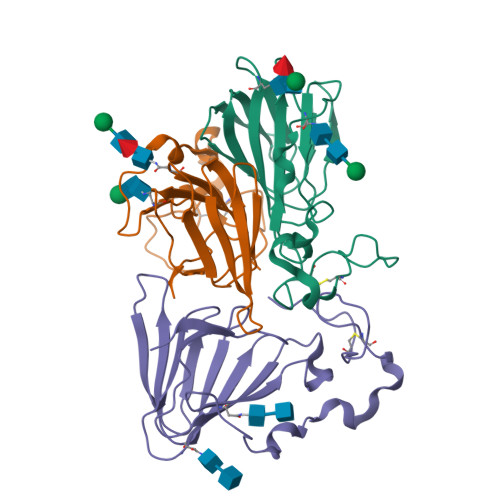
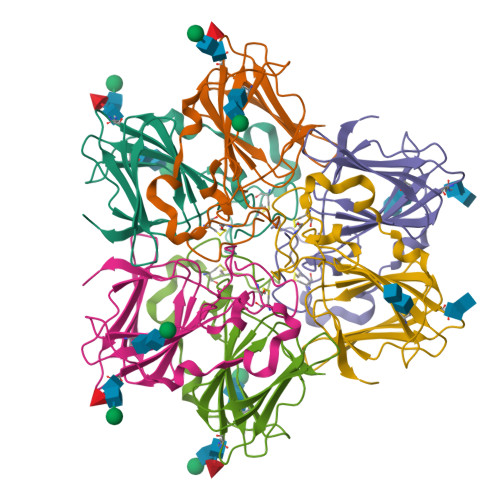
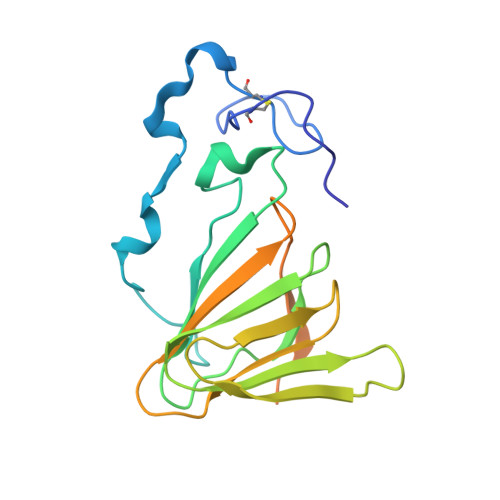
Peruvianin-I is a cysteine peptidase (EC 3.4.22) purified from Thevetia peruviana. Previous studies have shown that it is the only germin-like protein (GLP) with proteolytic activity described so far. In this work, the X-ray crystal structure of peruvianin-I was determined to a resolution of 2.15 Å (PDB accession number: 6ORM) and its specific location was evaluated by different assays. Its overall structure shows an arrangement composed of a homohexamer (a trimer of dimers) where each monomer exhibits a typical β-barrel fold and two glycosylation sites (Asn 55 and Asn 144 ). Analysis of its active site confirmed the absence of essential amino acids for typical oxalate oxidase activity of GLPs. Details of the active site and molecular docking results, using a specific cysteine peptidase inhibitor (iodoacetamide), were used to discuss a plausible mechanism for proteolytic activity of peruvianin-I. Histological analyses showed that T. peruviana has articulated anastomosing laticifers, i.e., rows of cells which merge to form continuous tubes throughout its green organs. Moreover, peruvianin-I was detected exclusively in the latex. Because latex peptidases have been described as defensive molecules against insects, we hypothesize that peruvianin-I contributes to protect T. peruviana plants against herbivory.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departamento de Bioquímica e Biologia Molecular, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Campus do Pici, CEP 60.440-554, Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil.