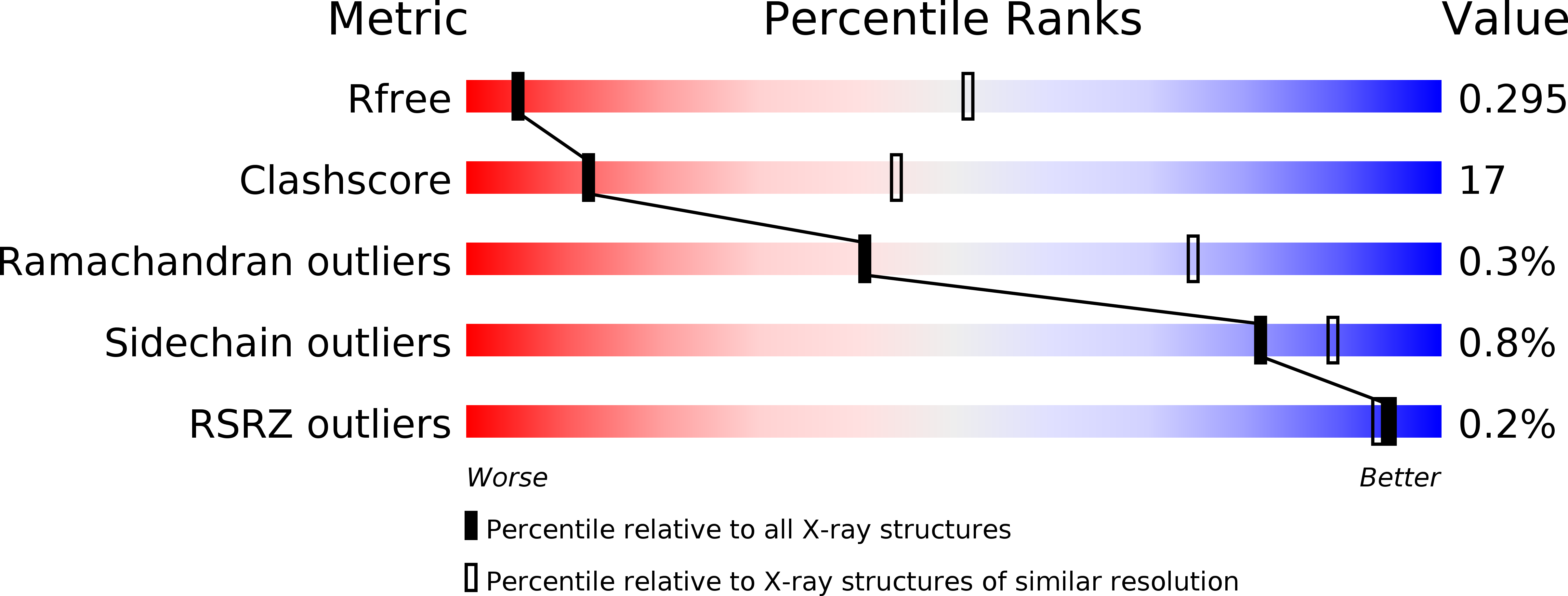
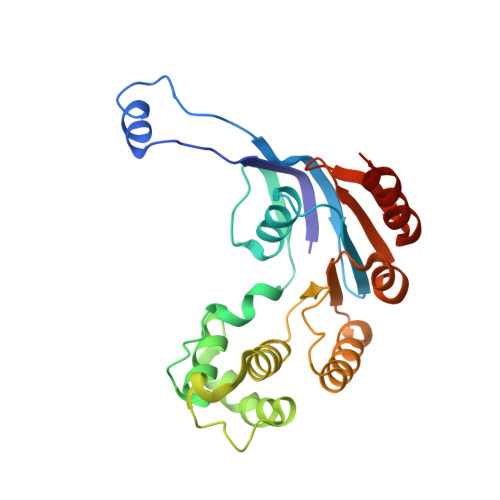
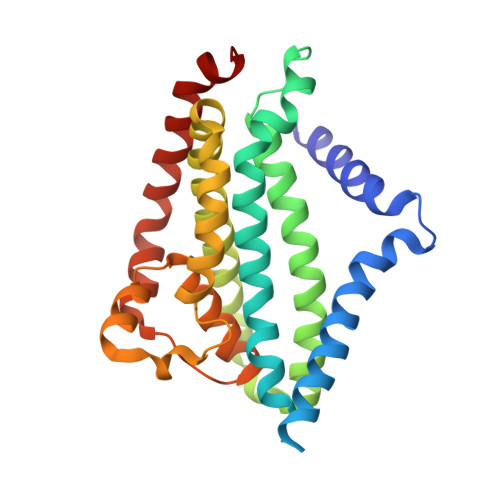
Architecture of a channel-forming O-antigen polysaccharide ABC transporter.
Bi, Y., Mann, E., Whitfield, C., Zimmer, J.(2018) Nature 553: 361-365
- PubMed: 29320481
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25190
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AMX, 6AN5, 6OIH - PubMed Abstract:
O-antigens are cell surface polysaccharides of many Gram-negative pathogens that aid in escaping innate immune responses. A widespread O-antigen biosynthesis mechanism involves the synthesis of the lipid-anchored polymer on the cytosolic face of the inner membrane, followed by transport to the periplasmic side where it is ligated to the lipid A core to complete a lipopolysaccharide molecule. In this pathway, transport to the periplasm is mediated by an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, called Wzm-Wzt. Here we present the crystal structure of the Wzm-Wzt homologue from Aquifex aeolicus in an open conformation. The transporter forms a transmembrane channel that is sufficiently wide to accommodate a linear polysaccharide. Its nucleotide-binding domain and a periplasmic extension form 'gate helices' at the cytosolic and periplasmic membrane interfaces that probably serve as substrate entry and exit points. Site-directed mutagenesis of the gates impairs in vivo O-antigen secretion in the Escherichia coli prototype. Combined with a closed structure of the isolated nucleotide-binding domains, our structural and functional analyses suggest a processive O-antigen translocation mechanism, which stands in contrast to the classical alternating access mechanism of ABC transporters.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia 22908, USA.