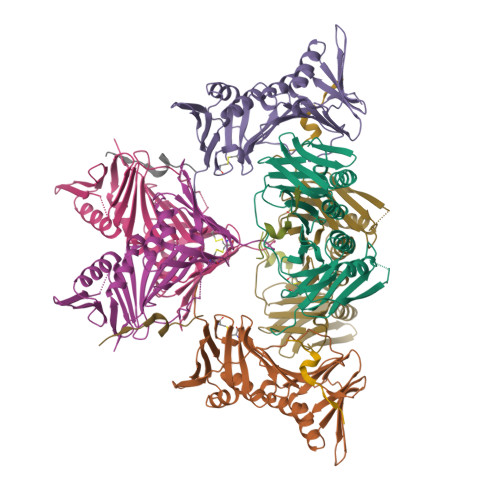
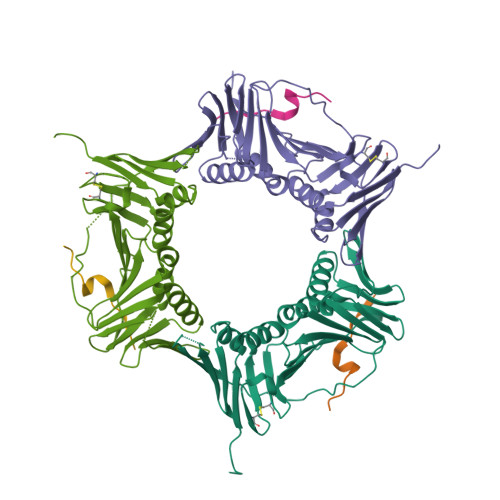
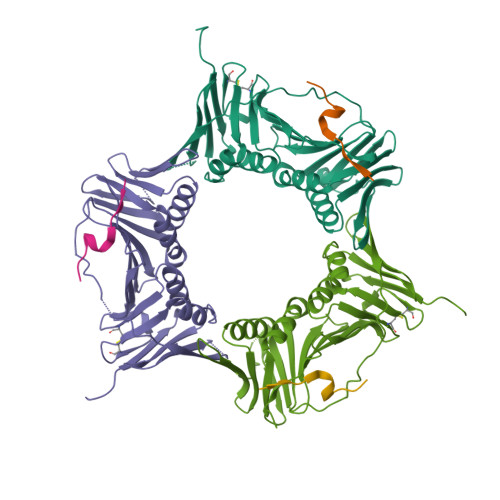
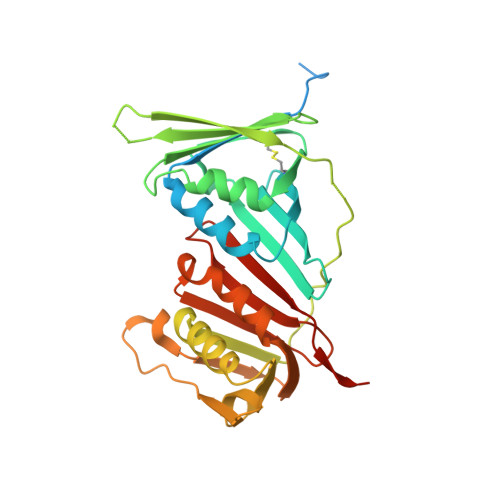
ATXR5/6 Forms Alternative Protein Complexes with PCNA and the Nucleosome Core Particle.
Davarinejad, H., Joshi, M., Ait-Hamou, N., Munro, K., Couture, J.F.(2019) J Mol Biology 431: 1370-1379
- PubMed: 30826376
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.02.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6O09 - PubMed Abstract:
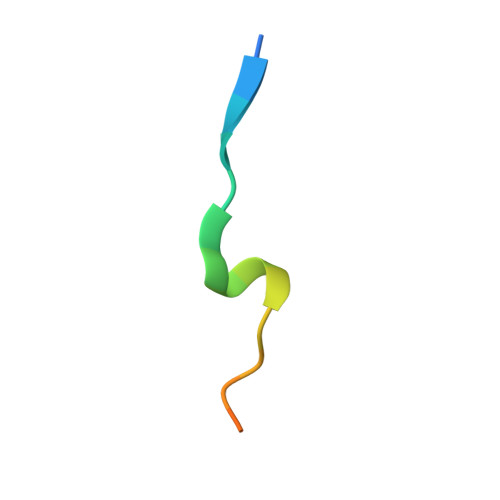
The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a sliding clamp associated with DNA polymerases and serves as a binding platform for the recruitment of regulatory proteins linked to DNA damage repair, cell cycle regulation, and epigenetic signaling. The histone H3 lysine-27 (H3K27) mono-methyltransferase Arabidopsis trithorax-related protein 5/6 (ATXR5/6) associates with PCNA, and this interaction has been proposed to act as a key determinant controlling the reestablishment of H3K27 mono-methylation following replication. In this study, we provide biochemical evidence showing that PCNA inhibits ATXR6 enzymatic activity. The structure of the ATXR6 PCNA-interacting peptide (PIP) in complex with PCNA indicates that a trio of hydrophobic residues contributes to the binding of the enzyme to the sliding clamp. Finally, despite the presence of three PIP binding clefts, only two molecules of ATXR6 bind to PCNA likely enabling the recruitment of a third protein to the sliding clamp. Collectively, these results rule out the model wherein PCNA-bound ATXR6 actively reestablishes H3K27 mono-methylation following DNA replication and provides insights into the role of ATXR6 PIP motif in its interaction with PCNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ottawa Institute of Systems Biology, Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology, University of Ottawa, 451 Smyth Road, Ottawa, ON K1H 8M5, Canada.