Rigidification Dramatically Improves Inhibitor Selectivity for RAF Kinases.
Assadieskandar, A., Yu, C., Maisonneuve, P., Kurinov, I., Sicheri, F., Zhang, C.(2019) ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1074-1080
- PubMed: 31312411
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00194
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NSQ - PubMed Abstract:
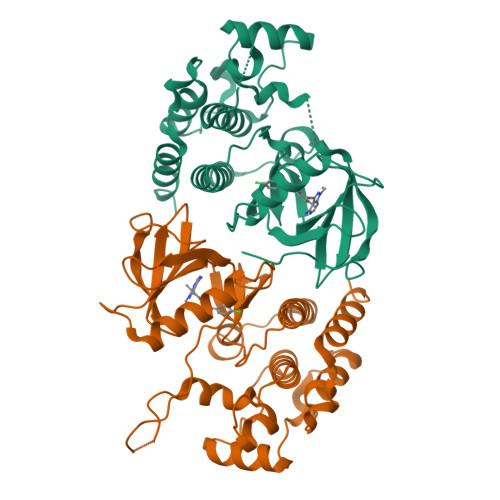
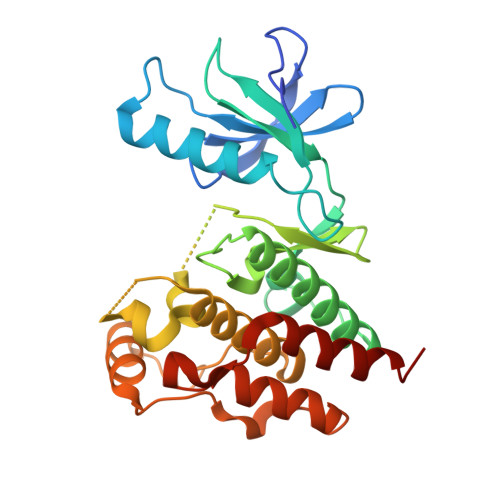
One effective means to achieve inhibitor specificity for RAF kinases, an important family of cancer drug targets, has been to target the monomeric inactive state conformation of the kinase domain, which, unlike most other kinases, can accommodate sulfonamide-containing drugs such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib because of the presence of a unique pocket specific to inactive RAF kinases. We previously reported an alternate strategy whereby rigidification of a nonselective pyrazolo[3,4- d ]pyrimidine-based inhibitor through ring closure afforded moderate but appreciable increases in selectivity for RAF kinases. Here, we show that a further application of the rigidification strategy to a different pyrazolopyrimidine-based scaffold dramatically improved selectivity for RAF kinases. Crystal structure analysis confirmed our inhibitor design hypothesis revealing that 2l engages an active-like state conformation of BRAF normally associated with poorly discriminating inhibitors. When screened against a panel of distinct cancer cell lines, the optimized inhibitor 2l primarily inhibited the proliferation of the expected BRAF V600E -harboring cell lines consistent with its kinome selectivity profile. These results suggest that rigidification could be a general and powerful strategy for enhancing inhibitor selectivity against protein kinases, which may open up therapeutic opportunities not afforded by other approaches.
Organizational Affiliation:
Loker Hydrocarbon Research Institute & Department of Chemistry, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California 90089, United States.