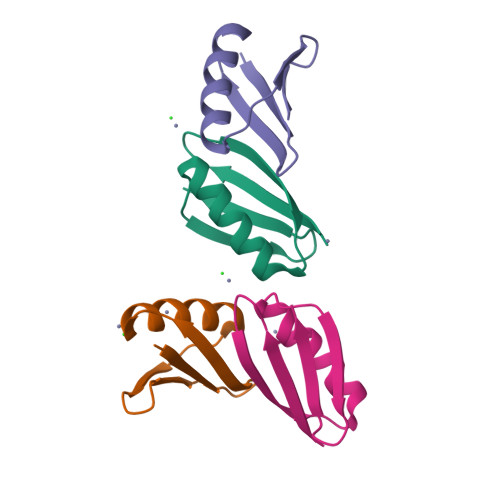
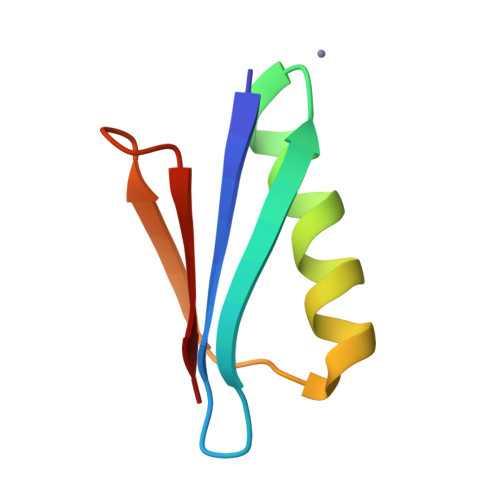
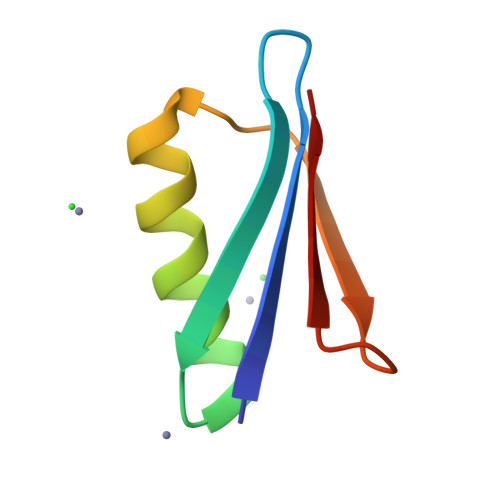
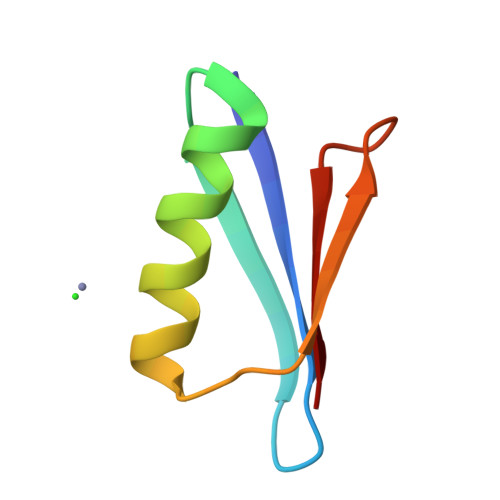
Design of High-Affinity Metal-Controlled Protein Dimers.
Maniaci, B., Lipper, C.H., Anipindi, D.L., Erlandsen, H., Cole, J.L., Stec, B., Huxford, T., Love, J.J.(2019) Biochemistry 58: 2199-2207
- PubMed: 30938154
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00055
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NL6, 6NL7, 6NL8, 6NL9, 6NLA, 6NLB - PubMed Abstract:
The ability to precisely control protein complex formation has high utility in the expanding field of biomaterials. Driving protein-protein binding through metal-ligand bridging interactions is a promising method of achieving this goal. Furthermore, the capacity to precisely regulate both complex formation and dissociation enables additional control not available with constitutive protein complexes. Here we describe the design of three metal-controlled protein dimers that are completely monomeric in the absence of metal yet form high-affinity symmetric homodimers in the presence of zinc sulfate. The scaffold used for the designed dimers is the β1 domain of streptococcal protein G. In addition to forming high-affinity dimers in the presence of metal, the complexes also dissociate upon addition of EDTA. Biophysical characterization revealed that the proteins maintain relatively high thermal stability, bind with high affinity, and are completely monodisperse in the monomeric and dimeric states. High-resolution crystal structures revealed that the dimers adopt the target structure and that the designed metal-binding histidine residues successfully bind zinc and function to drive dimer formation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry , San Diego State University , San Diego , California 92182 , United States.