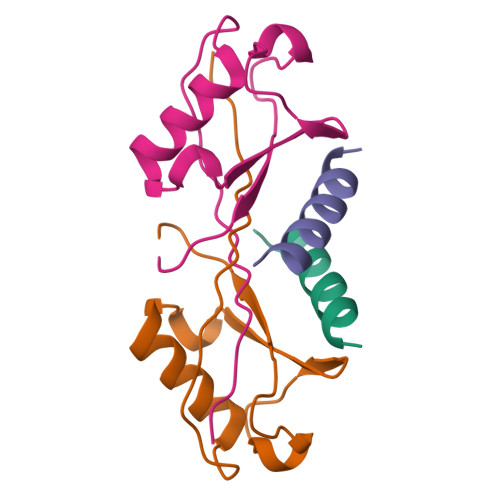
Dimerization of a ubiquitin variant leads to high affinity interactions with a ubiquitin interacting motif.
Manczyk, N., Veggiani, G., Gish, G.D., Yates, B.P., Ernst, A., Sidhu, S.S., Sicheri, F.(2019) Protein Sci 28: 848-856
- PubMed: 30793400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3593
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NJG - PubMed Abstract:
We previously described structural and functional characterization of the first ubiquitin variant (UbV), UbV.v27.1, engineered by phage display to bind with high affinity to a specific ubiquitin interacting motif (UIM). We identified two substitutions relative to ubiquitin (Gly10Val/His68Tyr) that were critical for enhancing binding affinity but could only rationalize the mechanism of action of the Tyr68 substitution. Here, we extend our characterization and uncover the mechanism by which the Val10 substitution enhances binding affinity. We show that Val10 in UbV.v27.1 drives UbV dimerization through an intermolecular β-strand exchange. Dimerization serves to increase the contact surface between the UIM and UbV and also affords direct contacts between two UIMs through an overall 2:2 binding stoichiometry. Our identification of the role of Val10 in UbV dimerization suggests a general means for the development of dimeric UbVs with improved affinity and specificity relative to their monomeric UbV counterparts. Statement: Previously, we used phage display to engineer a UbV that bound tightly and specifically to a UIM. Here, we discovered that tight binding is partly due to the dimerization of the UbV, which increases the contact surface between the UbV and UIM. We show that UbV dimerization is dependent on the Gly10Val substitution, and posit that dimerization may provide a general means for engineering UbVs with improved binding properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Ontario M5G 1X5, Canada.