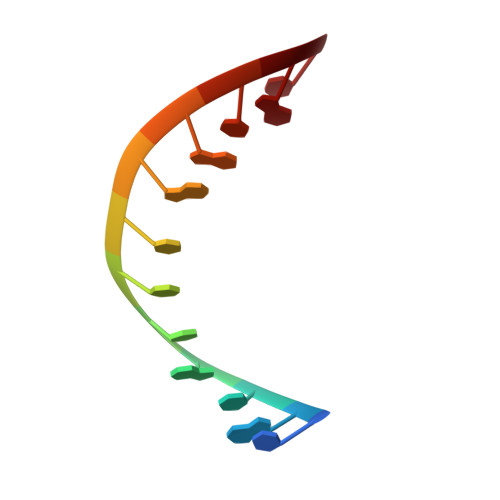
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Reveals That GU Base Pairs Flanking Internal Loops Can Adopt Diverse Structures.
Berger, K.D., Kennedy, S.D., Turner, D.H.(2019) Biochemistry 58: 1094-1108
- PubMed: 30702283
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01027
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6N8F, 6N8H, 6N8I - PubMed Abstract:
RNA thermodynamics play an important role in determining the two- and three-dimensional structures of RNA. Internal loops of the sequence 5'-GMNU/3'-UNMG are relatively unstable thermodynamically. Here, five duplexes with GU-flanked 2 × 2 nucleotide internal loops were structurally investigated to reveal determinants of their instability. The following internal loops were investigated: 5'-GCAU/3'-UACG, 5'-UUCG/3'-GCUU, 5'-GCUU/3'-UUCG, 5'-GUCU/3'-UCUG, and 5'-GCCU/3'-UCCG. Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectra indicate the absence of GU wobble base pairing in 5'-GCUU/3'-UUCG, 5'-GUCU/3'-UCUG, and 5'-GCCU/3'-UCCG. The 5'-GCUU/3'-UUCG loop has an unusual conformation of the GU base pairs, in which U's O2 carbonyl forms a bifurcated hydrogen bond with G's amino and imino protons. The internal loop of 5'-GUCU/3'-UCUG displays a shifted configuration in which GC pairs flank a U-U pair and several U's are in fast exchange between positions inside and outside the helix. In contrast, 5'-GCAU/3'-UACG and 5'-UUCG/3'-GCUU both have the expected GU wobble base pairs flanking the internal loop. Evidently, GU base pairs flanking internal loops are more likely to display atypical structures relative to Watson-Crick base pairs flanking internal loops. This appears to be more likely when the G of the GU pair is 5' to the loop. Such unusual structures could serve as recognition elements for biological function and as benchmarks for structure prediction methods.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics , University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry , Rochester , New York 14642 , United States.