An optimized chemical-genetic method for cell-specific metabolic labeling of RNA.
Nainar, S., Cuthbert, B.J., Lim, N.M., England, W.E., Ke, K., Sophal, K., Quechol, R., Mobley, D.L., Goulding, C.W., Spitale, R.C.(2020) Nat Methods 17: 311-318
- PubMed: 32015544
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0726-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
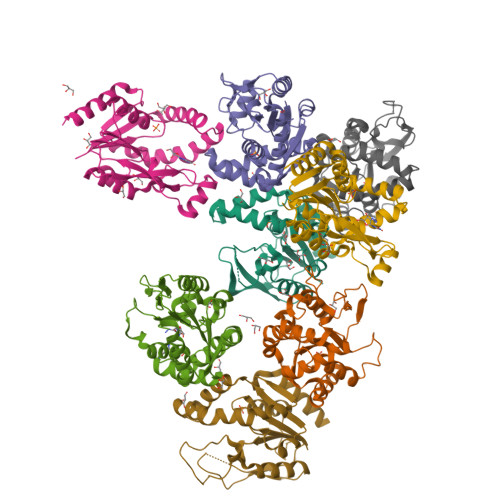
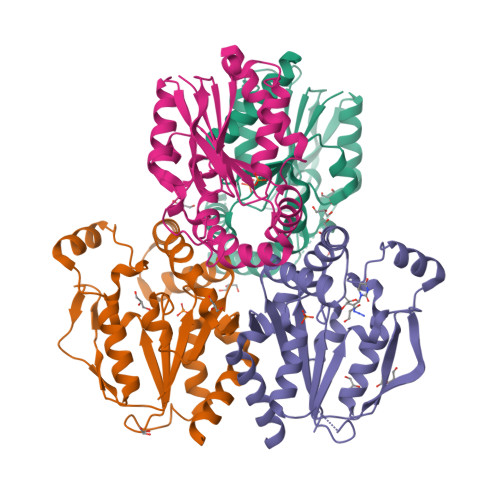
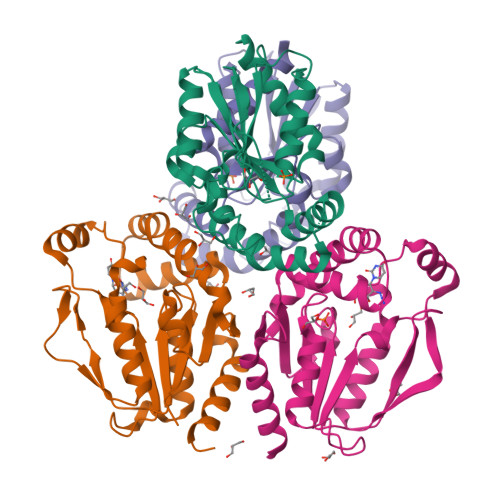
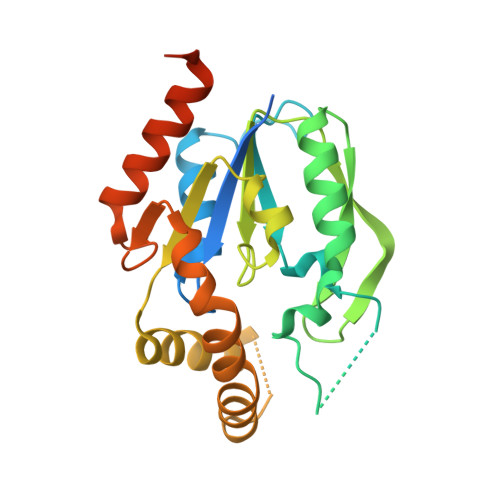
6N53, 6N54, 6N55 - PubMed Abstract:
Tissues and organs are composed of diverse cell types, which poses a major challenge for cell-type-specific profiling of gene expression. Current metabolic labeling methods rely on exogenous pyrimidine analogs that are only incorporated into RNA in cells expressing an exogenous enzyme. This approach assumes that off-target cells cannot incorporate these analogs. We disprove this assumption and identify and characterize the enzymatic pathways responsible for high background incorporation. We demonstrate that mammalian cells can incorporate uracil analogs and characterize the enzymatic pathways responsible for high background incorporation. To overcome these limitations, we developed a new small molecule-enzyme pair consisting of uridine/cytidine kinase 2 and 2'-azidouridine. We demonstrate that 2'-azidouridine is only incorporated in cells expressing uridine/cytidine kinase 2 and characterize selectivity mechanisms using molecular dynamics and X-ray crystallography. Furthermore, this pair can be used to purify and track RNA from specific cellular populations, making it ideal for high-resolution cell-specific RNA labeling. Overall, these results reveal new aspects of mammalian salvage pathways and serve as a new benchmark for designing, characterizing and evaluating methodologies for cell-specific labeling of biomolecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA.