Crystal structures of plant inorganic pyrophosphatase, an enzyme with a moonlighting autoproteolytic activity.
Grzechowiak, M., Ruszkowski, M., Sliwiak, J., Szpotkowski, K., Sikorski, M., Jaskolski, M.(2019) Biochem J 476: 2297-2319
- PubMed: 31371393
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20190427
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LS0, 6MT1, 6MT2 - PubMed Abstract:
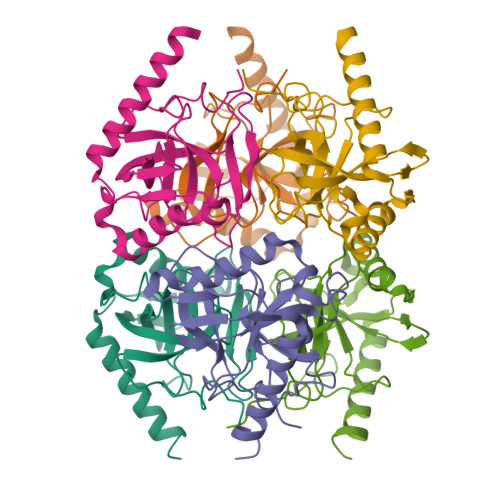
Inorganic pyrophosphatases (PPases, EC 3.6.1.1), which hydrolyze inorganic pyrophosphate to phosphate in the presence of divalent metal cations, play a key role in maintaining phosphorus homeostasis in cells. DNA coding inorganic pyrophosphatases from Arabidopsis thaliana ( At PPA1) and Medicago truncatula ( Mt PPA1) were cloned into a bacterial expression vector and the proteins were produced in Escherichia coli cells and crystallized. In terms of their subunit fold, At PPA1 and Mt PPA1 are reminiscent of other members of Family I soluble pyrophosphatases from bacteria and yeast. Like their bacterial orthologs, both plant PPases form hexamers, as confirmed in solution by multi-angle light scattering and size-exclusion chromatography. This is in contrast with the fungal counterparts, which are dimeric. Unexpectedly, the crystallized At PPA1 and Mt PPA1 proteins lack ∼30 amino acid residues at their N-termini, as independently confirmed by chemical sequencing. In vitro , self-cleavage of the recombinant proteins is observed after prolonged storage or during crystallization. The cleaved fragment corresponds to a putative signal peptide of mitochondrial targeting, with a predicted cleavage site at Val31-Ala32. Site-directed mutagenesis shows that mutations of the key active site Asp residues dramatically reduce the cleavage rate, which suggests a moonlighting proteolytic activity. Moreover, the discovery of autoproteolytic cleavage of a mitochondrial targeting peptide would change our perception of this signaling process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Biocrystallographic Research, Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poznan, Poland mgrzech@ibch.poznan.pl.