The Structure of a Peptide-Loaded Shark MHC Class I Molecule Reveals Features of the Binding between beta 2 -Microglobulin and H Chain Conserved in Evolution.
Wu, Y., Zhang, N., Wei, X., Lu, S., Li, S., Hashimoto, K., Dijkstra, J.M., Xia, C.(2021) J Immunol
- PubMed: 34145057
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2001165
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
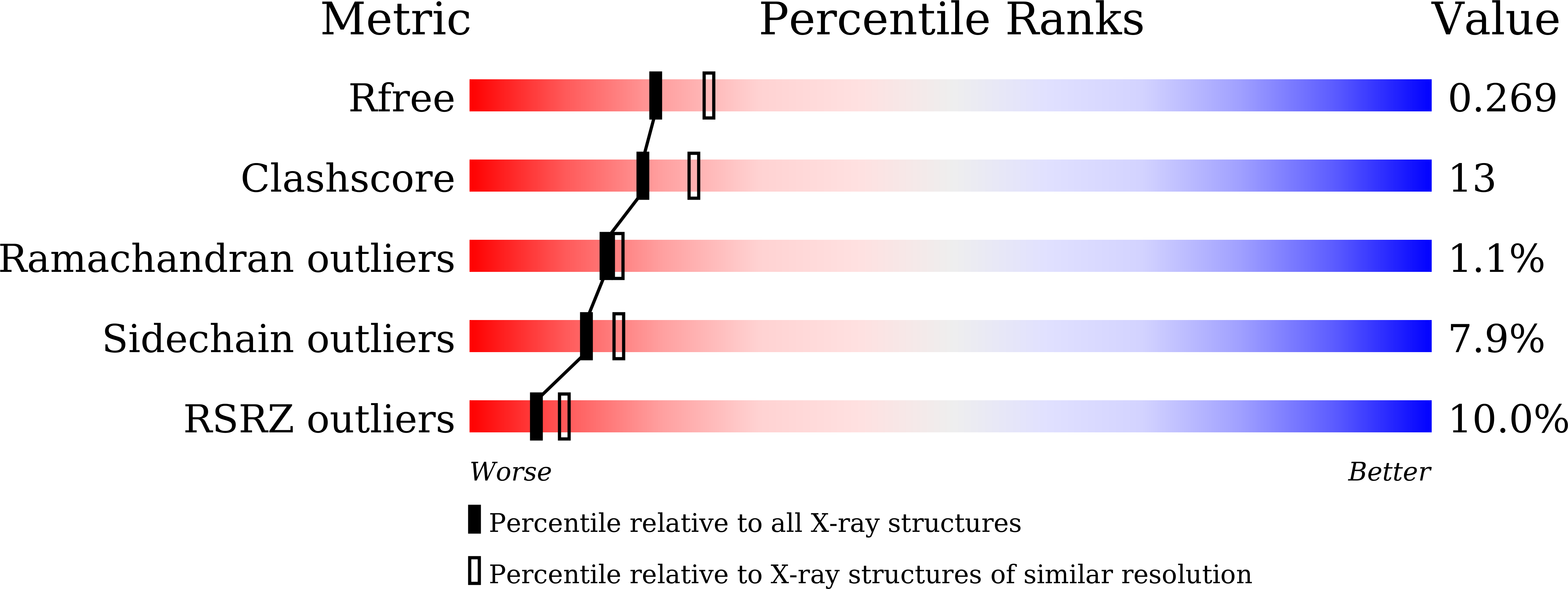
6LUO, 6LUP - PubMed Abstract:
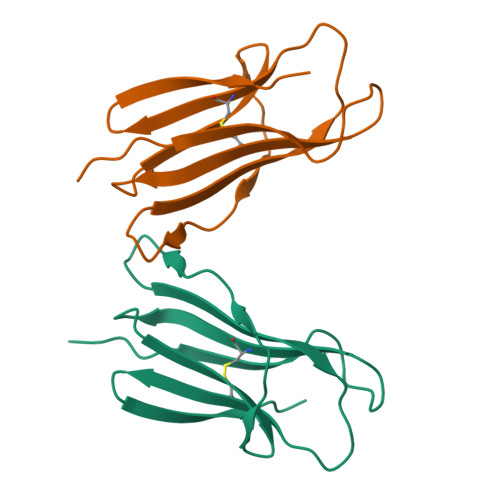
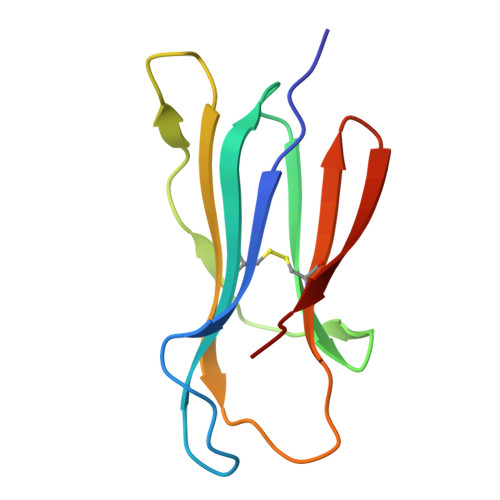
Cartilaginous fish are the most primitive extant species with MHC molecules. Using the nurse shark, the current study is, to the best of our knowledge, the first to present a peptide-loaded MHC class I (pMHC-I) structure for this class of animals. The overall structure was found to be similar between cartilaginous fish and bony animals, showing remarkable conservation of interactions between the three pMHC-I components H chain, β 2 -microglobulin (β 2 -m), and peptide ligand. In most previous studies, relatively little attention was given to the details of binding between the H chain and β 2 -m, and our study provides important new insights. A pronounced conserved feature involves the insertion of a large β 2 -m F56+W60 hydrophobic knob into a pleat of the β-sheet floor of the H chain α1α2 domain, with the knob being surrounded by conserved residues. Another conserved feature is a hydrogen bond between β 2 -m Y10 and a proline in the α3 domain of the H chain. By alanine substitution analysis, we found that the conserved β 2 -m residues Y10, D53, F56, and W60-each binding the H chain-are required for stable pMHC-I complex formation. For the β 2 -m residues Y10 and F56, such observations have not been reported before. The combined data indicate that for stable pMHC-I complex formation β 2 -m should not only bind the α1α2 domain but also the α3 domain. Knowing the conserved structural features of pMHC-I should be helpful for future elucidations of the mechanisms of pMHC-I complex formation and peptide editing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, College of Veterinary Medicine, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China; and.