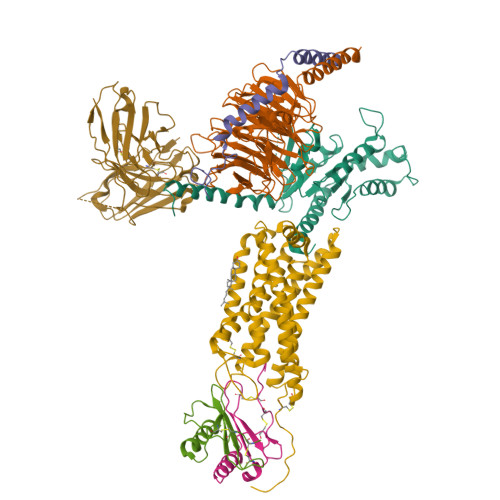
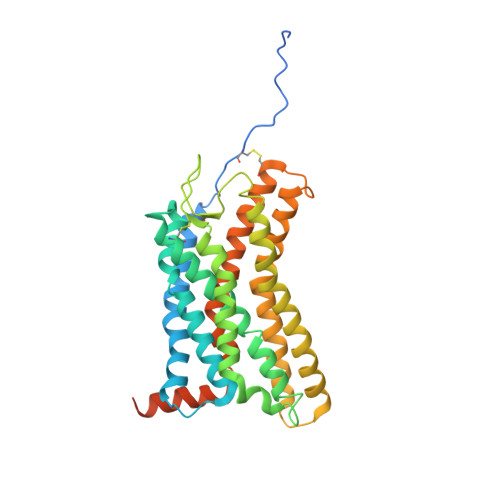
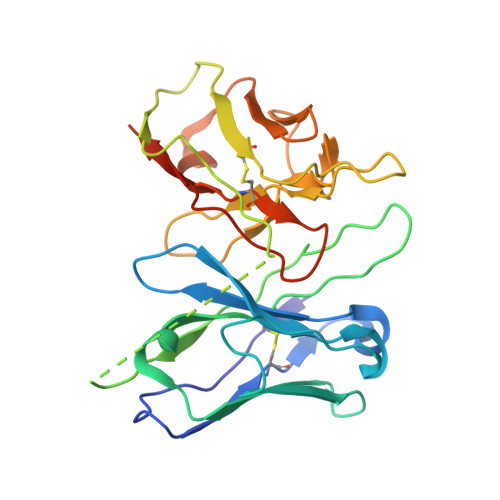
Structural basis of CXC chemokine receptor 2 activation and signalling.
Liu, K., Wu, L., Yuan, S., Wu, M., Xu, Y., Sun, Q., Li, S., Zhao, S., Hua, T., Liu, Z.J.(2020) Nature 585: 135-140
- PubMed: 32610344
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2492-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LFL, 6LFM, 6LFO - PubMed Abstract:
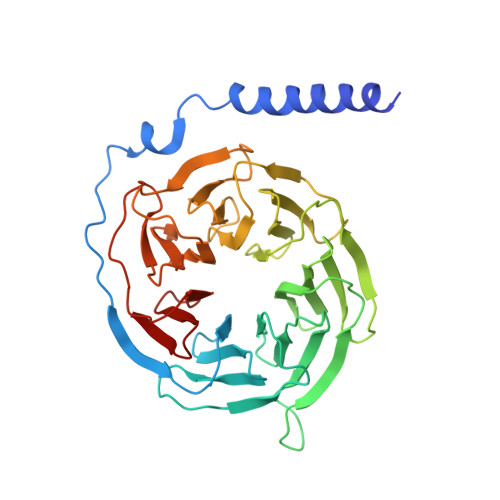
Chemokines and their receptors mediate cell migration, which influences multiple fundamental biological processes and disease conditions such as inflammation and cancer 1 . Although ample effort has been invested into the structural investigation of the chemokine receptors and receptor-chemokine recognition 2-4 , less is known about endogenous chemokine-induced receptor activation and G-protein coupling. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of interleukin-8 (IL-8, also known as CXCL8)-activated human CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) in complex with G i protein, along with a crystal structure of CXCR2 bound to a designed allosteric antagonist. Our results reveal a unique shallow mode of binding between CXCL8 and CXCR2, and also show the interactions between CXCR2 and G i protein. Further structural analysis of the inactive and active states of CXCR2 reveals a distinct activation process and the competitive small-molecule antagonism of chemokine receptors. In addition, our results provide insights into how a G-protein-coupled receptor is activated by an endogenous protein molecule, which will assist in the rational development of therapeutics that target the chemokine system for better pharmacological profiles.
Organizational Affiliation:
iHuman Institute, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China.