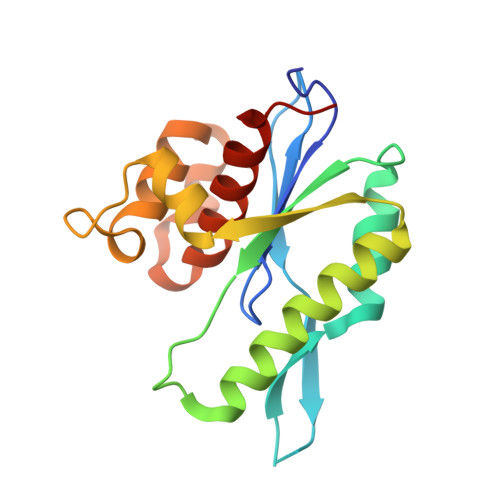
Structural insights into sequence-dependent Holliday junction resolution by the chloroplast resolvase MOC1.
Yan, J., Hong, S., Guan, Z., He, W., Zhang, D., Yin, P.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 1417-1417
- PubMed: 32184398
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15242-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KVN, 6KVO, 6LCM, 6LCT - PubMed Abstract:
Holliday junctions (HJs) are key DNA intermediates in genetic recombination and are eliminated by nuclease, termed resolvase, to ensure genome stability. HJ resolvases have been identified across all kingdoms of life, members of which exhibit sequence-dependent HJ resolution. However, the molecular basis of sequence selectivity remains largely unknown. Here, we present the chloroplast resolvase MOC1, which cleaves HJ in a cytosine-dependent manner. We determine the crystal structure of MOC1 with and without HJs. MOC1 exhibits an RNase H fold, belonging to the retroviral integrase family. MOC1 functions as a dimer, and the HJ is embedded into the basic cleft of the dimeric enzyme. We characterize a base recognition loop (BR loop) that protrudes into and opens the junction. Residues from the BR loop intercalate into the bases, disrupt the C-G base pairing at the crossover and recognize the cytosine, providing the molecular basis for sequence-dependent HJ resolution by a resolvase.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement and National Centre of Plant Gene Research, Huazhong Agricultural University, 430070, Wuhan, China.