Structural basis for the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by the SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein SPSB2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Li, K., You, T., Zhao, P., Luo, Y., Zhang, D., Wei, H., Wang, Y., Yang, J., Guan, X., Kuang, Z.(2021) Nitric Oxide 113-114: 1-6
- PubMed: 33862200
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2021.04.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KEY - PubMed Abstract:
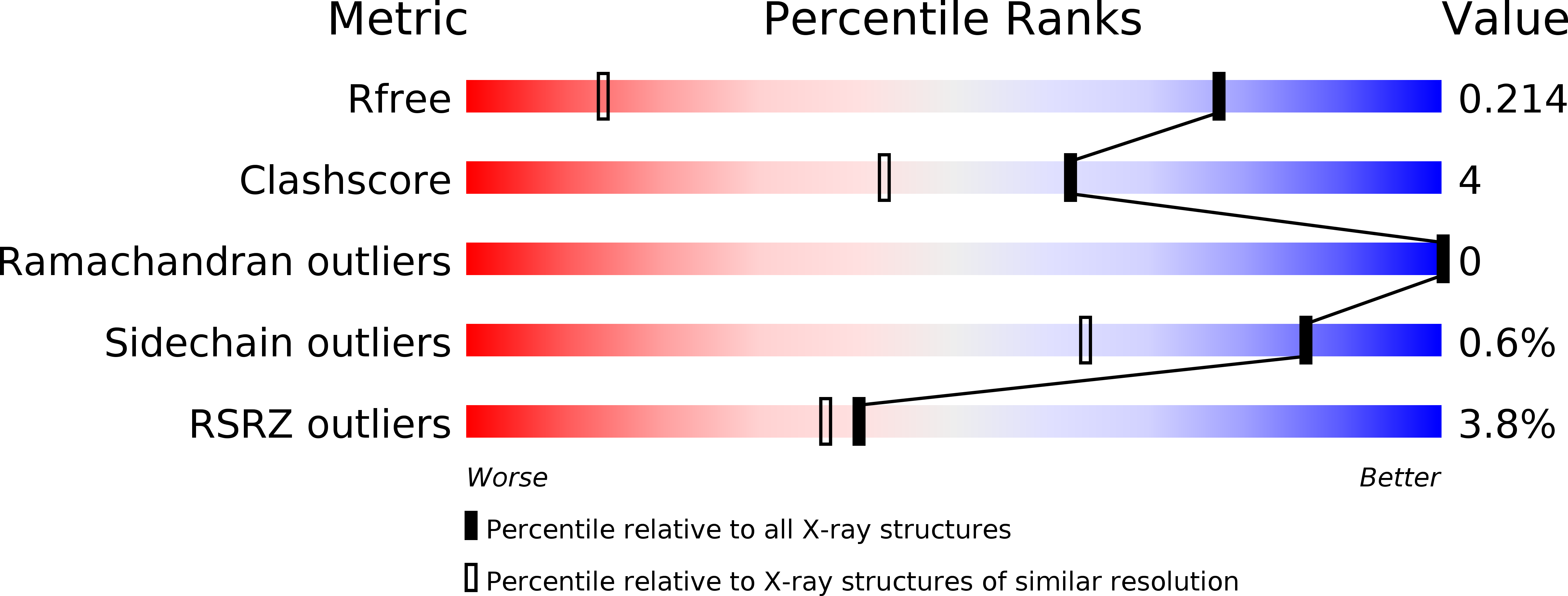
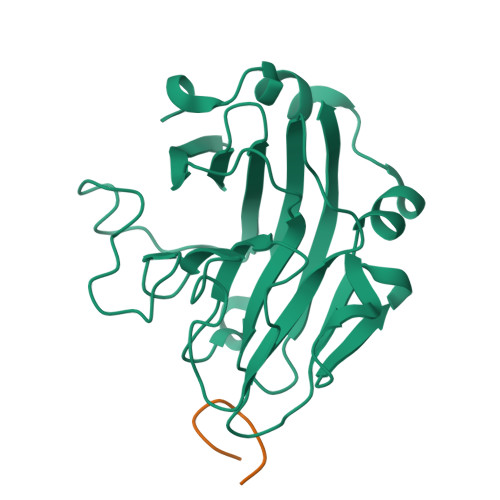
Relatively high concentration of nitric oxide (NO) produced by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in response to a variety of stimuli is a source of reactive nitrogen species, an important weapon of host innate immune defense. The SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 2 (SPSB2) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates the lifetime of iNOS. SPSB2 interacts with the N-terminal region of iNOS via a binding site on the SPRY domain of SPSB2, and recruits an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to polyubiquitinate iNOS, leading to its proteasomal degradation. Although critical residues for the SPSB2-iNOS interaction have been identified, structural basis for the interaction remains to be explicitly determined. In this study, we have determined a crystal structure of the N-terminal region of iNOS in complex with the SPRY domain of SPSB2 at 1.24 Å resolution. We have resolved the roles of some flanking residues, whose contribution to the SPSB2-iNOS interaction was structurally unclear previously. Furthermore, we have evaluated the effects of SPSB2 inhibitors on NO production using transient transfection and cell-penetrating peptide approaches, and found that such inhibitors can elevate NO production in RAW264.7 macrophages. These results thus provide a useful basis for the development of potent SPSB2 inhibitors as well as recruiting ligands for proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell Biology, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou, 510632, China; Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Bioengineering Medicine, Guangzhou, 510632, China; Guangdong Provincial Biotechnology Drug and Engineering Technology Research Center, Guangzhou, 510632, China; National Engineering Research Center of Genetic Medicine, Guangzhou, 510632, China.