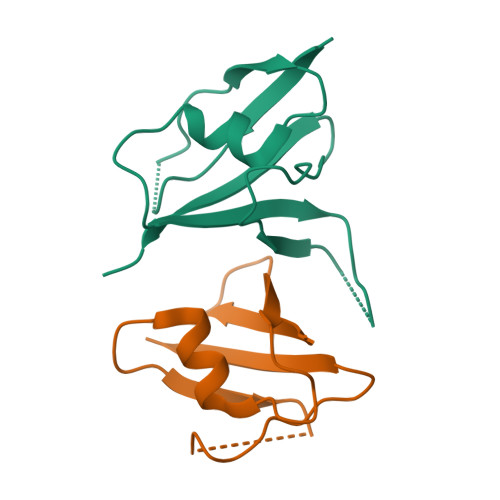
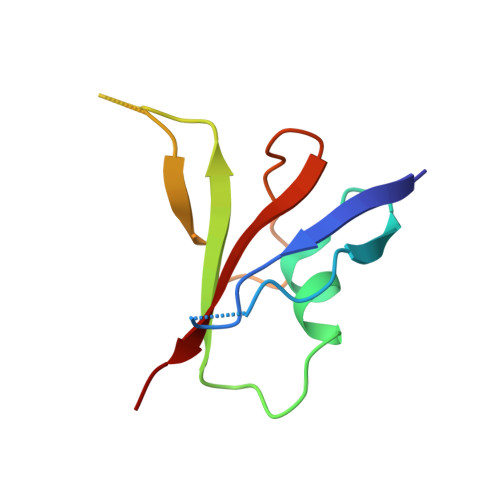
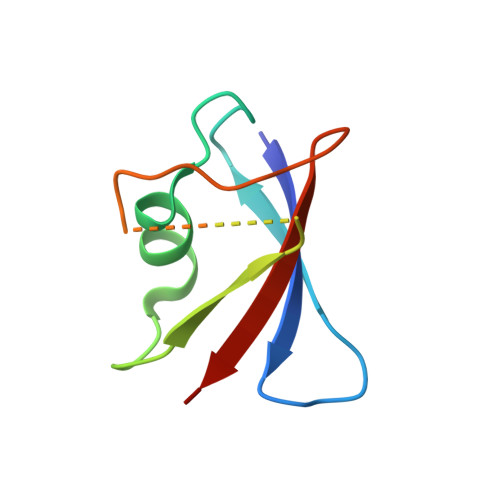
A direct heterotypic interaction between the DIX domains of Dishevelled and Axin mediates signaling to beta-catenin.
Yamanishi, K., Fiedler, M., Terawaki, S.I., Higuchi, Y., Bienz, M., Shibata, N.(2019) Sci Signal 12
- PubMed: 31822591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaw5505
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JCK - PubMed Abstract:
The Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway regulates embryonic development and tissue homeostasis throughout the animal kingdom. Signaling through this pathway crucially depends on the opposing activities of two cytoplasmic multiprotein complexes: the Axin destruction complex, which destabilizes the downstream effector β-catenin, and the Dishevelled signalosome, which inactivates the Axin complex and thus enables β-catenin to accumulate and operate a transcriptional switch in the nucleus. These complexes are assembled by dynamic head-to-tail polymerization of the DIX domains of Axin or Dishevelled, respectively, which increases their avidity for signaling effectors. Axin also binds to Dishevelled through its DIX domain. Here, we report the crystal structure of the heterodimeric complex between the two DIX domains of Axin and Dishevelled. This heterotypic interface resembles the interfaces observed in the individual homopolymers, albeit exhibiting a slight rearrangement of electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds, consistent with the heterotypic interaction being favored over the homotypic Axin DIX interaction. Last, cell-based signaling assays showed that heterologous polymerizing domains functionally substituted for the DIX domain of Dishevelled provided that these Dishevelled chimeras retained a DIX head or tail surface capable of binding to Axin. These findings indicate that the interaction between Dishevelled and Axin through their DIX domains is crucial for signaling to β-catenin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Picobiology, Graduate School of Life Science, University of Hyogo, 3-2-1 Koto, Kamigori-cho, Ako-gun, Hyogo 678-1297, Japan.