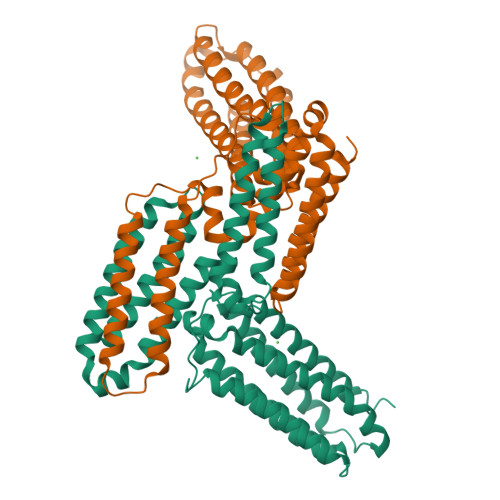
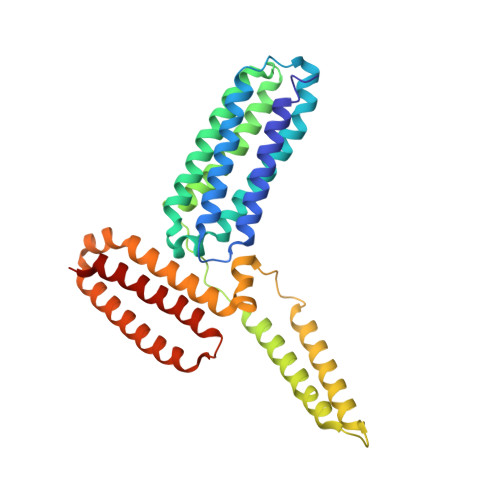
Talaromyces marneffeiMp1 Protein, a Novel Virulence Factor, Carries Two Arachidonic Acid-Binding Domains To Suppress Inflammatory Responses in Hosts.
Lam, W.H., Sze, K.H., Ke, Y., Tse, M.K., Zhang, H., Woo, P.C.Y., Lau, S.K.P., Lau, C.C.Y., Xu, S., Lai, P.M., Zhou, T., Antonyuk, S.V., Kao, R.Y.T., Yuen, K.Y., Hao, Q.(2019) Infect Immun 87
- PubMed: 30670555
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00679-18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5E7X, 5ECF, 6J6F - PubMed Abstract:
Talaromyces marneffei infection causes talaromycosis (previously known as penicilliosis), a very important opportunistic systematic mycosis in immunocompromised patients. Different virulence mechanisms in T. marneffei have been proposed and investigated. In the sera of patients with talaromycosis, Mp1 protein (Mp1p), a secretory galactomannoprotein antigen with two tandem ligand-binding domains (Mp1p-LBD1 and Mp1p-LBD2), was found to be abundant. Mp1p-LBD2 was reported to possess a hydrophobic cavity to bind copurified palmitic acid (PLM). It was hypothesized that capturing of lipids from human hosts by expressing a large quantity of Mp1p is a virulence mechanism of T. marneffei It was shown that expression of Mp1p enhanced the intracellular survival of T. marneffei by suppressing proinflammatory responses. Mechanistic study of Mp1p-LBD2 suggested that arachidonic acid (AA), a precursor of paracrine signaling molecules for regulation of inflammatory responses, is the major physiological target of Mp1p-LBD2. In this study, we use crystallographic and biochemical techniques to further demonstrate that Mp1p-LBD1, the previously unsolved first lipid binding domain of Mp1p, is also a strong AA-binding domain in Mp1p. These studies on Mp1p-LBD1 support the idea that the highly expressed Mp1p is an effective AA-capturing protein. Each Mp1p can bind up to 4 AA molecules. The crystal structure of Mp1p-LBD1-LBD2 has also been solved, showing that both LBDs are likely to function independently with a flexible linker between them. T. marneffei and potentially other pathogens highly expressing and secreting proteins similar to Mp1p can severely disturb host signaling cascades during proinflammatory responses by reducing the availabilities of important paracrine signaling molecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.