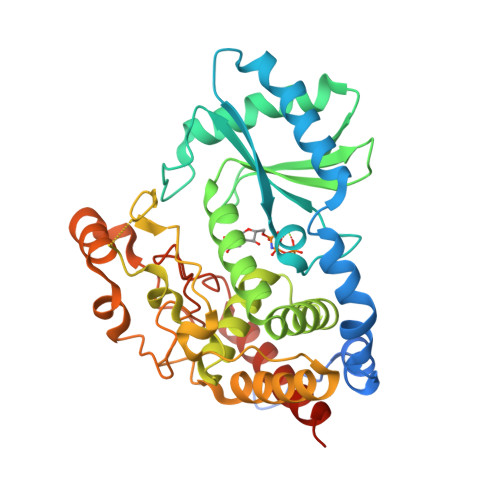
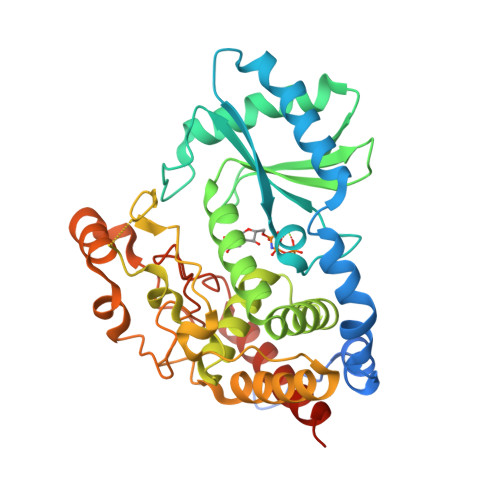
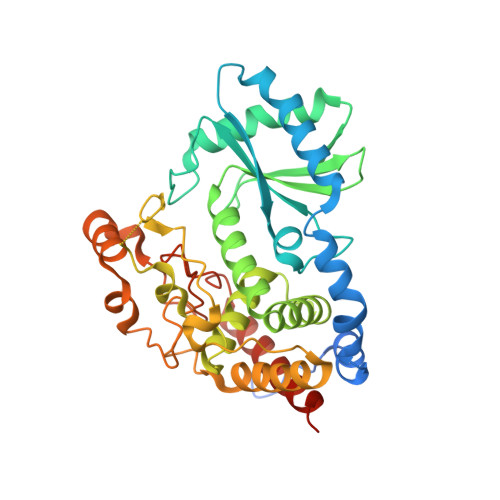
Structural basis for acceptor RNA substrate selectivity of the 3' terminal uridylyl transferase Tailor.
Kroupova, A., Ivascu, A., Reimao-Pinto, M.M., Ameres, S.L., Jinek, M.(2019) Nucleic Acids Res 47: 1030-1042
- PubMed: 30462292
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1164
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6I0S, 6I0T, 6I0U, 6I0V - PubMed Abstract:
Non-templated 3'-uridylation of RNAs has emerged as an important mechanism for regulating the processing, stability and biological function of eukaryotic transcripts. In Drosophila, oligouridine tailing by the terminal uridylyl transferase (TUTase) Tailor of numerous RNAs induces their degradation by the exonuclease Dis3L2, which serves functional roles in RNA surveillance and mirtron RNA biogenesis. Tailor preferentially uridylates RNAs terminating in guanosine or uridine nucleotides but the structural basis underpinning its RNA substrate selectivity is unknown. Here, we report crystal structures of Tailor bound to a donor substrate analog or mono- and oligouridylated RNA products. These structures reveal specific amino acid residues involved in donor and acceptor substrate recognition, and complementary biochemical assays confirm the critical role of an active site arginine in conferring selectivity toward 3'-guanosine terminated RNAs. Notably, conservation of these active site features suggests that other eukaryotic TUTases, including mammalian TUT4 and TUT7, might exhibit similar, hitherto unknown, substrate selectivity. Together, these studies provide critical insights into the specificity of 3'-uridylation in eukaryotic post-transcriptional gene regulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Zurich, Zurich 8057, Switzerland.