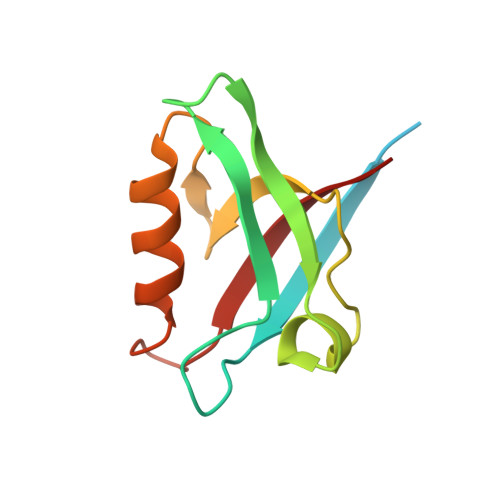
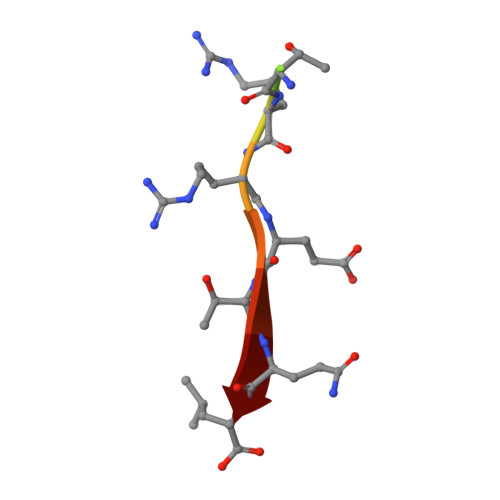
Structural and functional characterization of the PDZ domain of the human phosphatase PTPN3 and its interaction with the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein.
Genera, M., Samson, D., Raynal, B., Haouz, A., Baron, B., Simenel, C., Guerois, R., Wolff, N., Caillet-Saguy, C.(2019) Sci Rep 9: 7438-7438
- PubMed: 31092861
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43932-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HKS - PubMed Abstract:
The human protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 3 (PTPN3) is a PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1) domain-containing phosphatase with a tumor-suppressive or a tumor-promoting role in many cancers. Interestingly, the high-risk genital human papillomavirus (HPV) types 16 and 18 target the PDZ domain of PTPN3. The presence of a PDZ binding motif (PBM) on E6 confers interaction with a number of different cellular PDZ domain-containing proteins and is a marker of high oncogenic potential. Here, we report the molecular basis of interaction between the PDZ domain of PTPN3 and the PBM of the HPV E6 protein. We combined biophysical, NMR and X-ray experiments to investigate the structural and functional properties of the PDZ domain of PTPN3. We showed that the C-terminal sequences from viral proteins encompassing a PBM interact with PTPN3-PDZ with similar affinities to the endogenous PTPN3 ligand MAP kinase p38γ. PBM binding stabilizes the PDZ domain of PTPN3. We solved the X-ray structure of the PDZ domain of PTPN3 in complex with the PBM of the HPV E6 protein. The crystal structure and the NMR chemical shift mapping of the PTPN3-PDZ/peptide complex allowed us to pinpoint the main structural determinants of recognition of the C-terminal sequence of the E6 protein and the long-range perturbations induced upon PBM binding.
- Récepteurs-Canaux, Institut Pasteur, UMR 3571, CNRS, F-75724, Paris, France.
Organizational Affiliation: