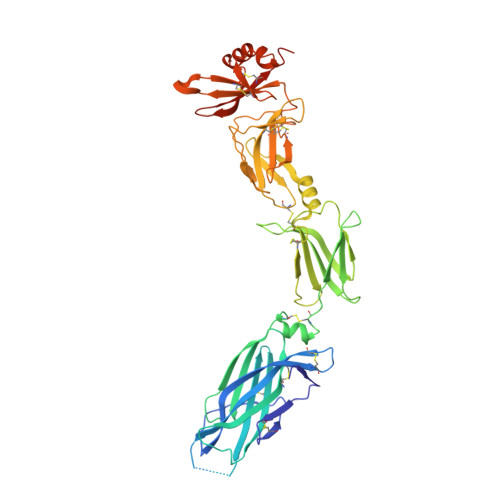
Structural Analysis Reveals that the Cytokine IL-17F Forms a Homodimeric Complex with Receptor IL-17RC to Drive IL-17RA-Independent Signaling.
Goepfert, A., Lehmann, S., Blank, J., Kolbinger, F., Rondeau, J.M.(2020) Immunity 52: 499-512.e5
- PubMed: 32187518
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.02.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HG4, 6HG9, 6HGA, 6HGO, 6HGU - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), IL-17F, and IL-17A/F heterodimers are key cytokines of the innate and adaptive immune response. Dysregulation of the IL-17 pathway contributes to immune pathology, and it is therefore important to elucidate the molecular mechanisms that govern IL-17 recognition and signaling. The receptor IL-17RC is thought to act in concert with IL-17RA to transduce IL-17A-, IL-17F-, and IL-17A/F-mediated signals. We report the crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human IL-17RC in complex with IL-17F. In contrast to the expected model, we found that IL-17RC formed a symmetrical 2:1 complex with IL-17F, thus competing with IL-17RA for cytokine binding. Using biophysical techniques, we showed that IL-17A and IL-17A/F also form 2:1 complexes with IL-17RC, suggesting the possibility of IL-17RA-independent IL-17 signaling pathways. The crystal structure of the IL-17RC:IL-17F complex provides a structural basis for IL-17F signaling through IL-17RC, with potential therapeutic applications for respiratory allergy and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, Novartis Pharma AG, 4002 Basel, Switzerland.