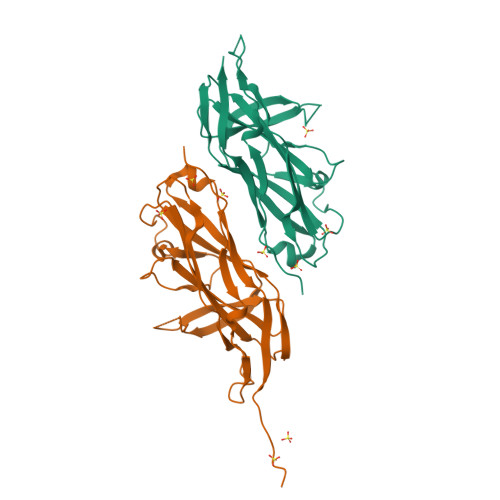
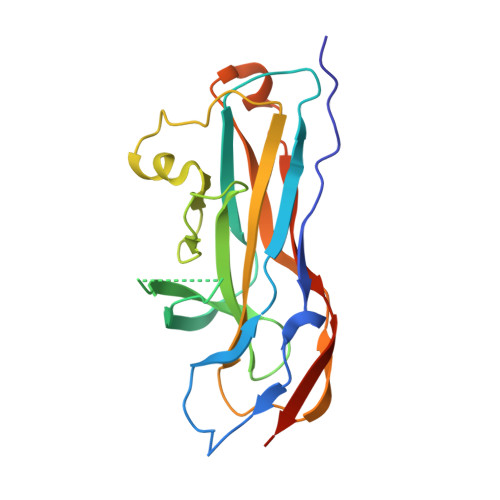
Structures of two fimbrial adhesins, AtfE and UcaD, from the uropathogen Proteus mirabilis.
Jiang, W., Ubhayasekera, W., Pearson, M.M., Knight, S.D.(2018) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 74: 1053-1062
- PubMed: 30387764
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318012391
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H1Q, 6H1X, 6H2L - PubMed Abstract:
The important uropathogen Proteus mirabilis encodes a record number of chaperone/usher-pathway adhesive fimbriae. Such fimbriae, which are used for adhesion to cell surfaces/tissues and for biofilm formation, are typically important virulence factors in bacterial pathogenesis. Here, the structures of the receptor-binding domains of the tip-located two-domain adhesins UcaD (1.5 Å resolution) and AtfE (1.58 Å resolution) from two P. mirabilis fimbriae (UCA/NAF and ATF) are presented. The structures of UcaD and AtfE are both similar to the F17G type of tip-located fimbrial receptor-binding domains, and the structures are very similar despite having only limited sequence similarity. These structures represent an important step towards a molecular-level understanding of P. mirabilis fimbrial adhesins and their roles in the complex pathogenesis of urinary-tract infections.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Uppsala University, Biomedical Center, PO Box 596, SE-751 24 Uppsala, Sweden.