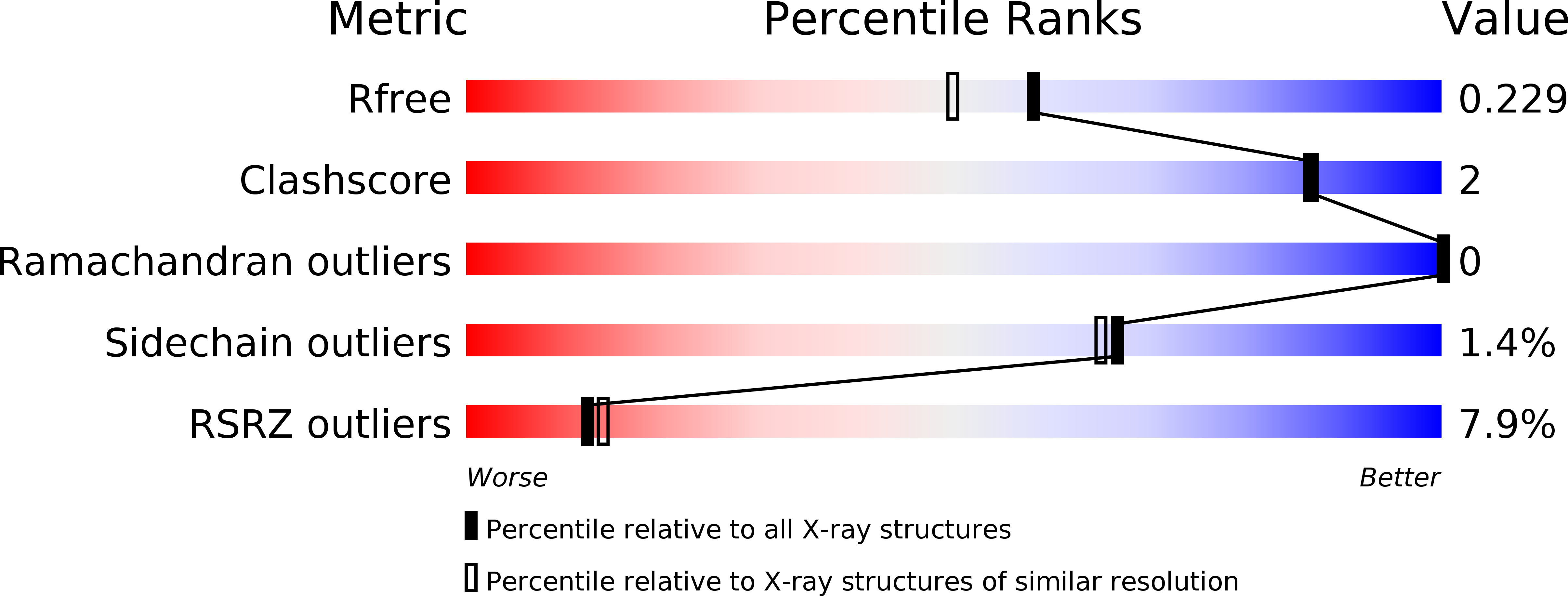
X-ray structures of human bile-salt activated lipase conjugated to nerve agents surrogates.
Touvrey, C., Courageux, C., Guillon, V., Terreux, R., Nachon, F., Brazzolotto, X.(2019) Toxicology 411: 15-23
- PubMed: 30359675
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2018.10.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H0T, 6H0V, 6H18, 6H19, 6H1A - PubMed Abstract:
The efficiency of human butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) as a stoichiometric bioscavenger of nerve agents is well established. However, wide use is currently limited by production and purification costs. Aiming at identifying an alternative human protein bioscavenger, we looked for an original scaffold candidate by virtual screening of the Protein Data Bank for functional similarity using the "Surfing the Molecules" software (sumo-pbil.ibcp.fr) and a search model based on the BChE active site topology. Besides the expected acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase, we identified a set of bile salt activated lipases structures, among which the human pancreatic lipase (hBAL) that shares 34% identity with BChE. We produced the recombinant enzyme in mammalian cells, purified it, and measured the inhibition constants for paraoxon and surrogates of VX, sarin and tabun. We solved the X-ray structure of apo hBAL and conjugates with paraoxon and the surrogates at resolutions in the 2-Å range. These structures allow the assessment of hBAL for scavenging nerve agents. They revealed that hBAL has inverted stereoselectivity for the surrogates of nerve agent compared to human cholinesterases. We observed a remarkable flip of the catalytic histidine driven by the chelation of Zn 2+ . Dealkylation of the conjugate, aka aging, was solely observed for paraoxon.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Biologie et Chimie des Protéines, 7 Passage du Vercors, 69367 Lyon Cedex 07, France.