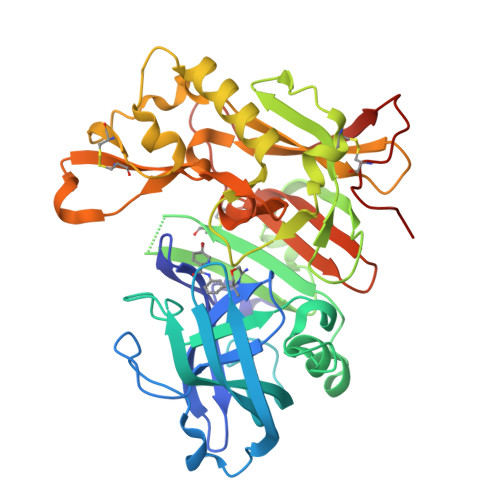
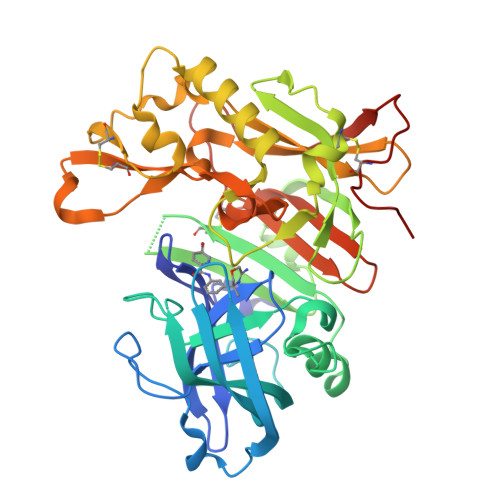
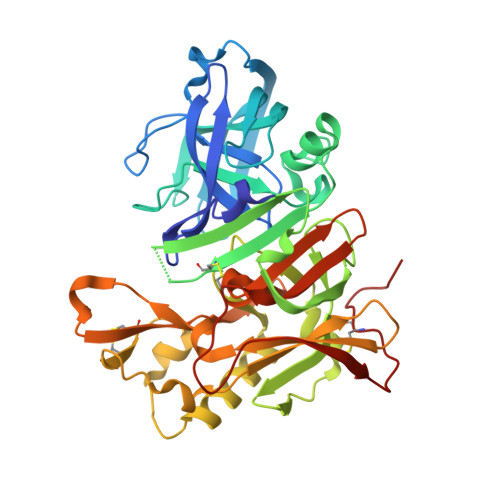
Discovery of amino-1,4-oxazines as potent BACE-1 inhibitors.
Veenstra, S.J., Rueeger, H., Voegtle, M., Lueoend, R., Holzer, P., Hurth, K., Tintelnot-Blomley, M., Frederiksen, M., Rondeau, J.M., Jacobson, L., Staufenbiel, M., Neumann, U., Machauer, R.(2018) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 2195-2200
- PubMed: 29764741
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.05.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FGY - PubMed Abstract:
New amino-1,4-oxazine derived BACE-1 inhibitors were explored and various synthetic routes developed. The binding mode of the inhibitors was elucidated by co-crystallization of 4 with BACE-1 and X-ray analysis. Subsequent optimization led to inhibitors with low double digit nanomolar activity in a biochemical and single digit nanomolar potency in a cellular assays. To assess the inhibitors for their permeation properties and potential to cross the blood-brain-barrier a MDR1-MDCK cell model was successfully applied. Compound 8a confirmed the in vitro results by dose-dependently reducing Aβ levels in mice in an acute treatment regimen.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Global Discovery Chemistry, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, Novartis Pharma AG, CH-4057 Basel, Switzerland.