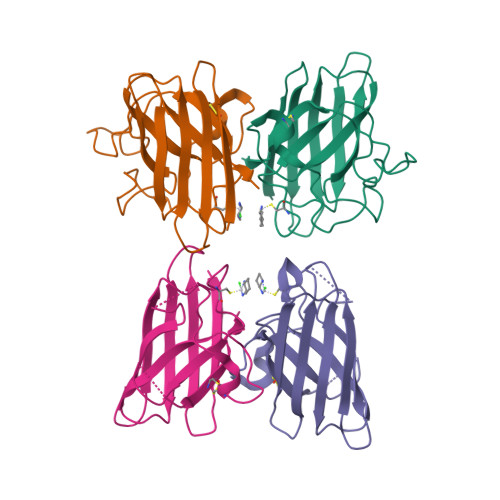
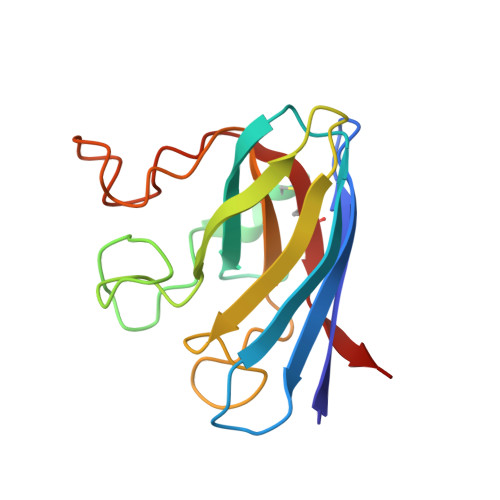
Interaction of Half Oxa-/Halfcis-Platin Complex with Human Superoxide Dismutase and Induced Reduction of Neurotoxicity.
Cantini, F., Calderone, V., Di Cesare Mannelli, L., Korsak, M., Gonnelli, L., Francesconi, O., Ghelardini, C., Banci, L., Nativi, C.(2018) ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 1094-1098
- PubMed: 30429951
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00199
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FFK - PubMed Abstract:
The formation of amorphous protein aggregates containing human superoxide dismutase (hSOD1) is thought to be involved in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis onset. cis -Platin inhibits the oligomerization of apo hSOD1, but its toxicity precludes any possible use in therapy. Herein, we propose a less toxic platinum complex, namely oxa/ cis -platin, as hSOD1 antiaggregation lead compound. Oxa/ cis -platin is able to interact with hSOD1 in the disulfide oxidized apo form by binding cysteine 111 (Cys111). The mild neurotoxic phenomena induced in vitro and in vivo by oxa/ cis -platin can be successfully reverted by using lypoyl derivatives, which do not interfere with the antiaggregation properties of the platin derivative.
Organizational Affiliation:
Dipartimento di Chimica "Ugo Schiff", University of Florence, via della Lastruccia, 3-13 50019 Sesto Fiorentino (FI), Italy.