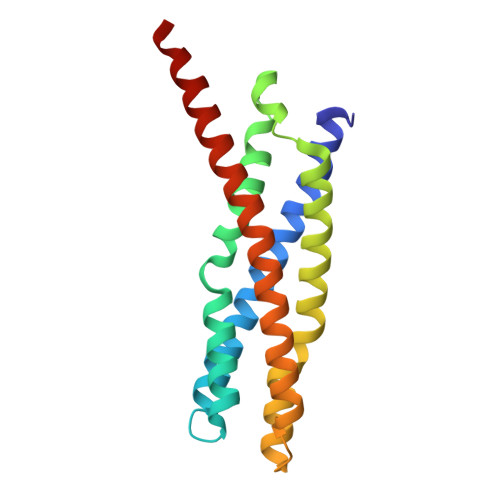
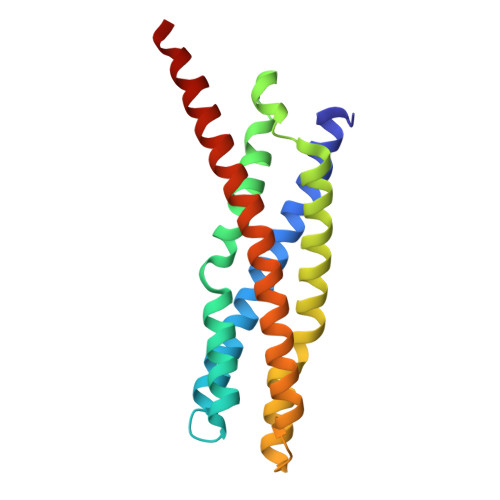
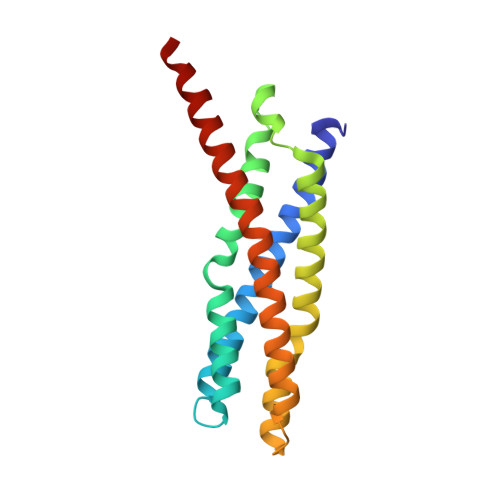
Structural basis for the homotypic fusion of chlamydial inclusions by the SNARE-like protein IncA.
Cingolani, G., McCauley, M., Lobley, A., Bryer, A.J., Wesolowski, J., Greco, D.L., Lokareddy, R.K., Ronzone, E., Perilla, J.R., Paumet, F.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 2747-2747
- PubMed: 31227715
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10806-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6E6A, 6E7E - PubMed Abstract:
Many intracellular bacteria, including Chlamydia, establish a parasitic membrane-bound organelle inside the host cell that is essential for the bacteria's survival. Chlamydia trachomatis forms inclusions that are decorated with poorly characterized membrane proteins known as Incs. The prototypical Inc, called IncA, enhances Chlamydia pathogenicity by promoting the homotypic fusion of inclusions and shares structural and functional similarity to eukaryotic SNAREs. Here, we present the atomic structure of the cytoplasmic domain of IncA, which reveals a non-canonical four-helix bundle. Structure-based mutagenesis, molecular dynamics simulation, and functional cellular assays identify an intramolecular clamp that is essential for IncA-mediated homotypic membrane fusion during infection.
Organizational Affiliation:
Thomas Jefferson University, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Philadelphia, PA, 19107, USA. gino.cingolani@jefferson.edu.