Structure of the IFN gamma receptor complex guides design of biased agonists.
Mendoza, J.L., Escalante, N.K., Jude, K.M., Sotolongo Bellon, J., Su, L., Horton, T.M., Tsutsumi, N., Berardinelli, S.J., Haltiwanger, R.S., Piehler, J., Engleman, E.G., Garcia, K.C.(2019) Nature 567: 56-60
- PubMed: 30814731
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0988-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6E3K, 6E3L - PubMed Abstract:
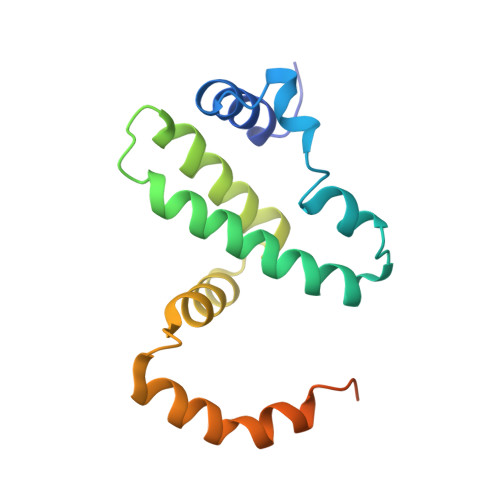
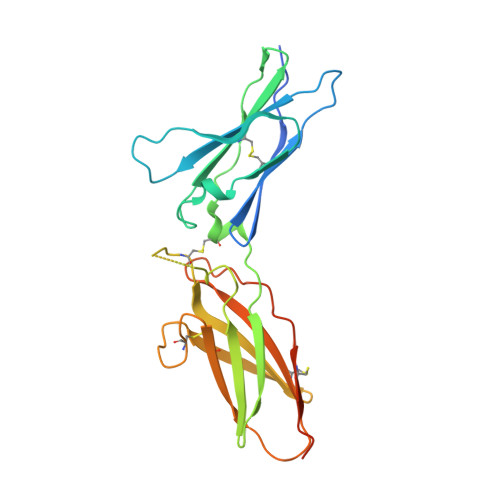
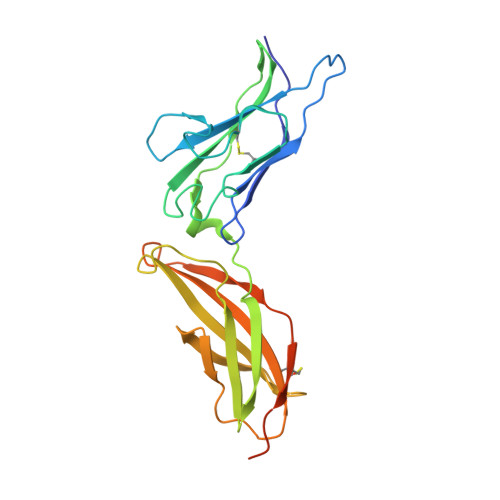
The cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ) is a central coordinator of innate and adaptive immunity, but its highly pleiotropic actions have diminished its prospects for use as an immunotherapeutic agent. Here, we took a structure-based approach to decoupling IFNγ pleiotropy. We engineered an affinity-enhanced variant of the ligand-binding chain of the IFNγ receptor IFNγR1, which enabled us to determine the crystal structure of the complete hexameric (2:2:2) IFNγ-IFNγR1-IFNγR2 signalling complex at 3.25 Å resolution. The structure reveals the mechanism underlying deficits in IFNγ responsiveness in mycobacterial disease syndrome resulting from a T168N mutation in IFNγR2, which impairs assembly of the full signalling complex. The topology of the hexameric complex offers a blueprint for engineering IFNγ variants to tune IFNγ receptor signalling output. Unexpectedly, we found that several partial IFNγ agonists exhibited biased gene-expression profiles. These biased agonists retained the ability to induce upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression, but exhibited impaired induction of programmed death-ligand 1 expression in a wide range of human cancer cell lines, offering a route to decoupling immunostimulatory and immunosuppressive functions of IFNγ for therapeutic applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.