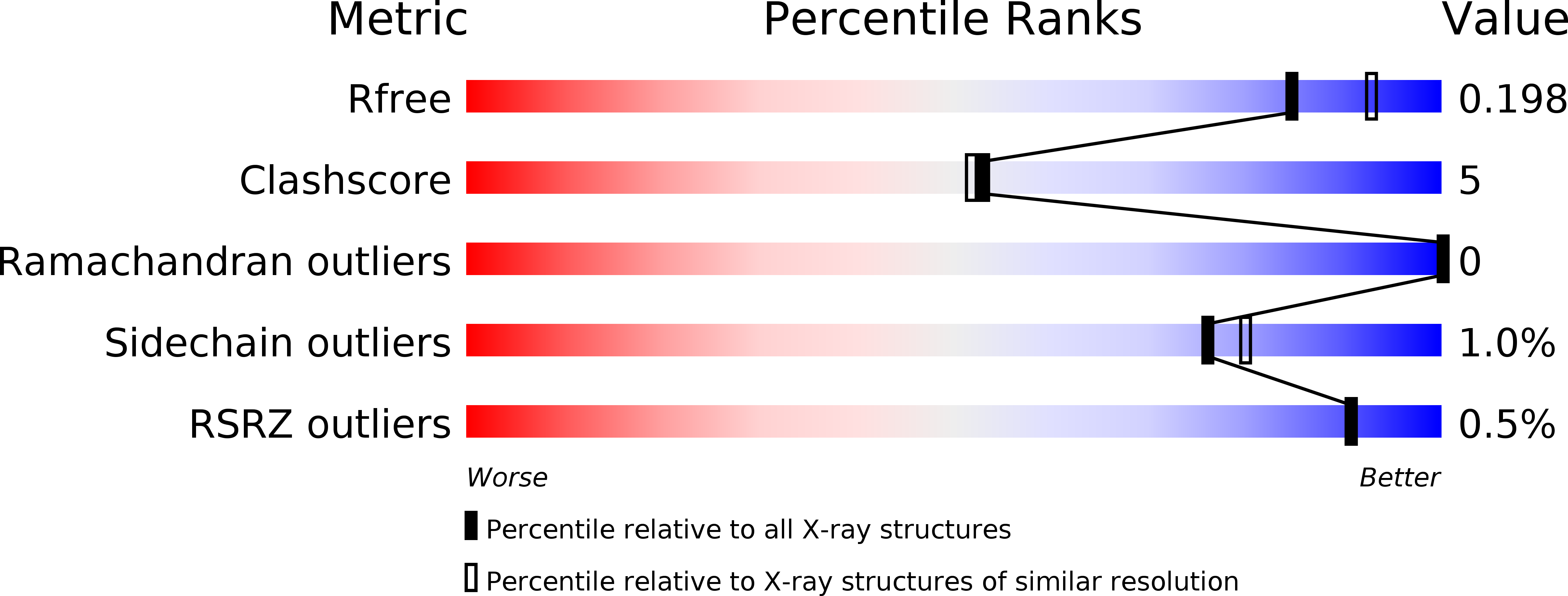
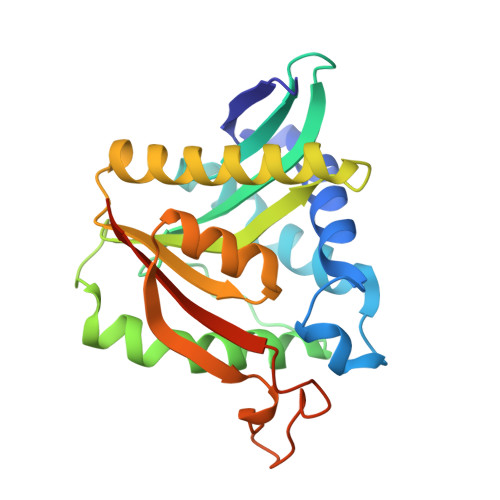
Drosophila melanogasternonribosomal peptide synthetase Ebony encodes an atypical condensation domain.
Izore, T., Tailhades, J., Hansen, M.H., Kaczmarski, J.A., Jackson, C.J., Cryle, M.J.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 2913-2918
- PubMed: 30705105
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1811194116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DYM, 6DYN, 6DYO, 6DYR, 6DYS - PubMed Abstract:
The protein Ebony from Drosophila melanogaster plays a central role in the regulation of histamine and dopamine in various tissues through condensation of these amines with β-alanine. Ebony is a rare example of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) from a higher eukaryote and contains a C-terminal sequence that does not correspond to any previously characterized NRPS domain. We have structurally characterized this C-terminal domain and have discovered that it adopts the aryl-alkylamine- N -acetyl transferase (AANAT) fold, which is unprecedented in NRPS biology. Through analysis of ligand-bound structures, activity assays, and binding measurements, we have determined how this atypical condensation domain is able to provide selectivity for both the carrier protein-bound amino acid and the amine substrates, a situation that remains unclear for standard condensation domains identified to date from NRPS assembly lines. These results demonstrate that the C terminus of Ebony encodes a eukaryotic example of an alternative type of NRPS condensation domain; they also illustrate how the catalytic components of such assembly lines are significantly more diverse than a minimal set of conserved functional domains.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University, Clayton, VIC 3800, Australia; thierry.izore@monash.edu max.cryle@monash.edu.