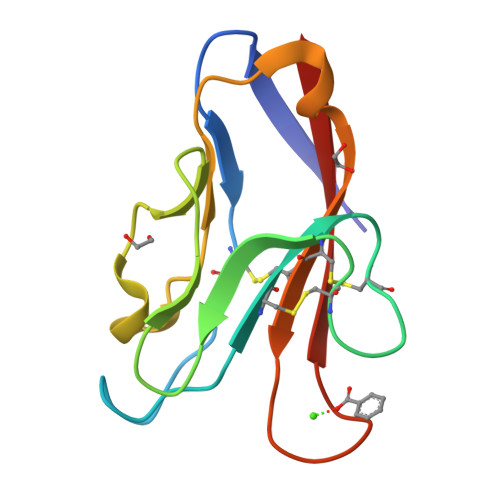
High resolution X-ray and NMR structural study of human T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-3.
Gandhi, A.K., Kim, W.M., Sun, Z.J., Huang, Y.H., Bonsor, D.A., Sundberg, E.J., Kondo, Y., Wagner, G., Kuchroo, V.K., Petsko, G., Blumberg, R.S.(2018) Sci Rep 8: 17512-17512
- PubMed: 30504845
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35754-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DHB - PubMed Abstract:
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-3 (TIM-3) is an important immune regulator. Here, we describe a novel high resolution (1.7 Å) crystal structure of the human (h)TIM-3 N-terminal variable immunoglobulin (IgV) domain with bound calcium (Ca ++ ) that was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Significant conformational differences were observed in the B-C, C'-C″ and C'-D loops of hTIM-3 compared to mouse (m)TIM-3, hTIM-1 and hTIM-4. Further, the conformation of the C-C' loop of hTIM-3 was notably different from hTIM-4. Consistent with the known metal ion-dependent binding of phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) to mTIM-3 and mTIM-4, the NMR spectral analysis and crystal structure of Ca ++ -bound hTIM-3 revealed that residues in the hTIM-3 F-G loop coordinate binding to Ca ++ . In addition, we established a novel biochemical assay to define hTIM-3 functionality as determined by binding to human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1). These studies provide new insights useful for understanding and targeting hTIM-3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, 75 Francis Street, Boston, MA, 02115, USA.