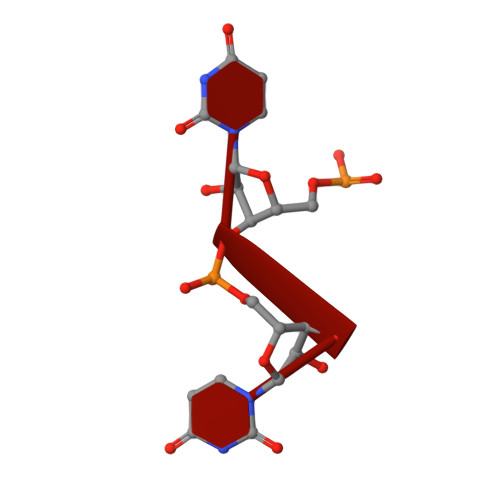
Structural and mechanistic basis for preferential deadenylation of U6 snRNA by Usb1.
Nomura, Y., Roston, D., Montemayor, E.J., Cui, Q., Butcher, S.E.(2018) Nucleic Acids Res 46: 11488-11501
- PubMed: 30215753
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky812
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6D2Z, 6D30, 6D31 - PubMed Abstract:
Post-transcriptional modification of snRNA is central to spliceosome function. Usb1 is an exoribonuclease that shortens the oligo-uridine tail of U6 snRNA, resulting in a terminal 2',3' cyclic phosphate group in most eukaryotes, including humans. Loss of function mutations in human Usb1 cause the rare disorder poikiloderma with neutropenia (PN), and result in U6 snRNAs with elongated 3' ends that are aberrantly adenylated. Here, we show that human Usb1 removes 3' adenosines with 20-fold greater efficiency than uridines, which explains the presence of adenylated U6 snRNAs in cells lacking Usb1. We determined three high-resolution co-crystal structures of Usb1: wild-type Usb1 bound to the substrate analog adenosine 5'-monophosphate, and an inactive mutant bound to RNAs with a 3' terminal adenosine and uridine. These structures, along with QM/MM MD simulations of the catalytic mechanism, illuminate the molecular basis for preferential deadenylation of U6 snRNA. The extent of Usb1 processing is influenced by the secondary structure of U6 snRNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA.