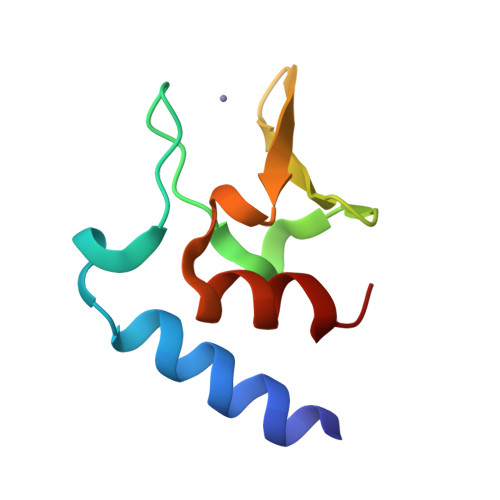
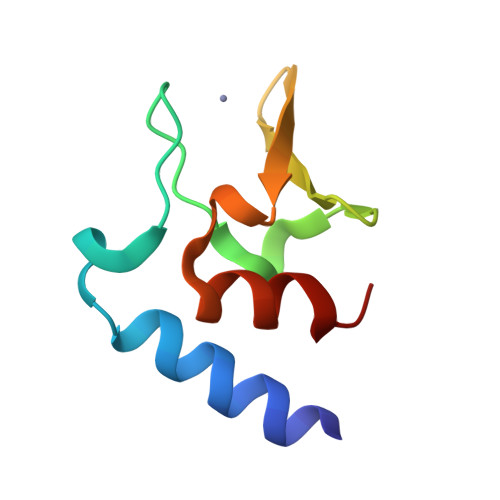
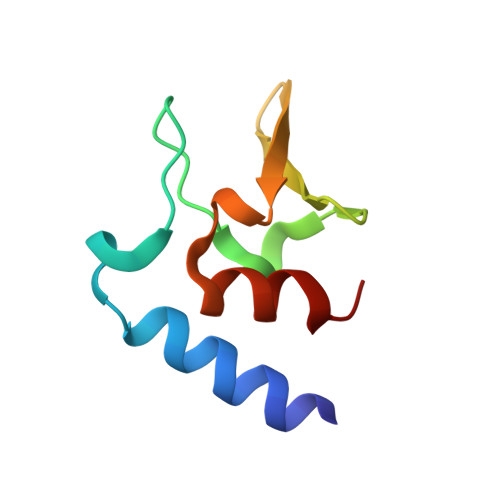
Structural characterisation of the HT3 motif of the polyhistidine triad protein D from Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Luo, Z., Pederick, V.G., Paton, J.C., McDevitt, C.A., Kobe, B.(2018) FEBS Lett 592: 2341-2350
- PubMed: 29856892
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CSL - PubMed Abstract:
The bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae (the pneumococcus) is a major human pathogen that requires Zn 2+ for its survival and virulence in the host environment. Polyhistidine triad protein D (PhtD) has a known role in pneumococcal Zn 2+ homeostasis. However, the mechanistic basis of PhtD function remains unclear, partly due to a lack of structural information. Here, we determined the crystal structure of the fragment PhtD 269-339 , containing the third Zn 2+ -binding histidine triad (HT) motif of the protein. Analysis of the structure suggests that Zn 2+ binding occurs at the surface of the protein and that all five HT motifs in the protein bind Zn 2+ and share similar structures. These new structural insights aid in our understanding of how the Pht proteins facilitate pneumococcal Zn 2+ acquisition.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.