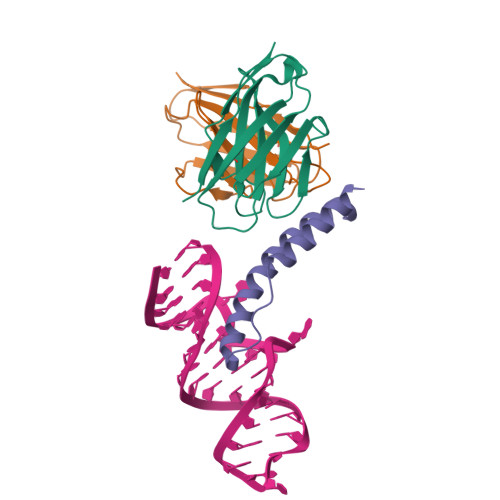
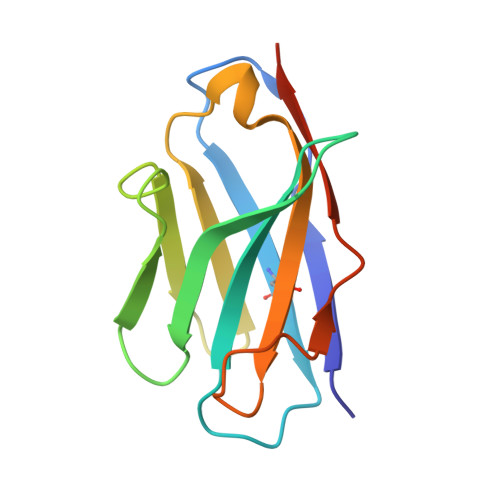
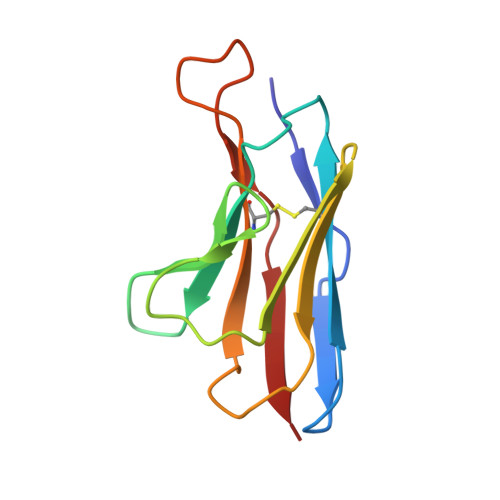
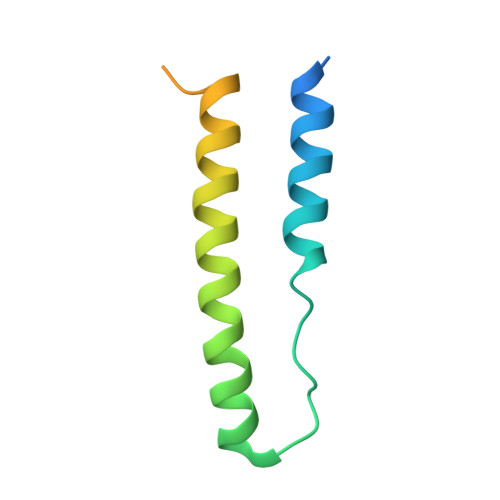
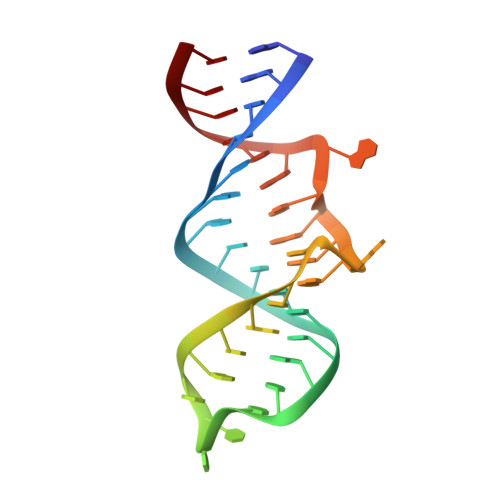
Structure of an RNA Aptamer that Can Inhibit HIV-1 by Blocking Rev-Cognate RNA (RRE) Binding and Rev-Rev Association.
Dearborn, A.D., Eren, E., Watts, N.R., Palmer, I.W., Kaufman, J.D., Steven, A.C., Wingfield, P.T.(2018) Structure 26: 1187
- PubMed: 30017564
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.06.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CF2 - PubMed Abstract:
HIV-1 Rev protein mediates nuclear export of unspliced and partially spliced viral RNAs for production of viral genomes and structural proteins. Rev assembles on a 351-nt Rev response element (RRE) within viral transcripts and recruits host export machinery. Small (<40-nt) RNA aptamers that compete with the RRE for Rev binding inhibit HIV-1 viral replication. We determined the X-ray crystal structure of a potential anti-HIV-1 aptamer that binds Rev with high affinity (K d = 5.9 nM). The aptamer is structurally similar to the RRE high-affinity site but forms additional contacts with Rev unique to its sequence. Exposed bases of the aptamer interleave with the guanidinium groups of two arginines of Rev, forming stacking interactions and hydrogen bonds. The aptamer also obstructs an oligomerization interface of Rev, blocking Rev self-assembly. We propose that this aptamer can inhibit HIV-1 replication by interfering with Rev-RRE, Rev-Rev, and possibly Rev-host protein interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Protein Expression Laboratory, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.