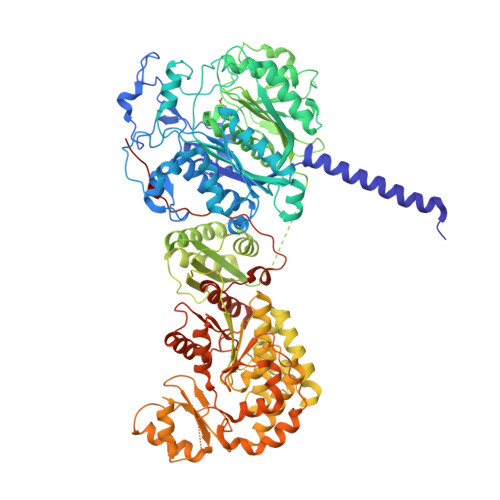
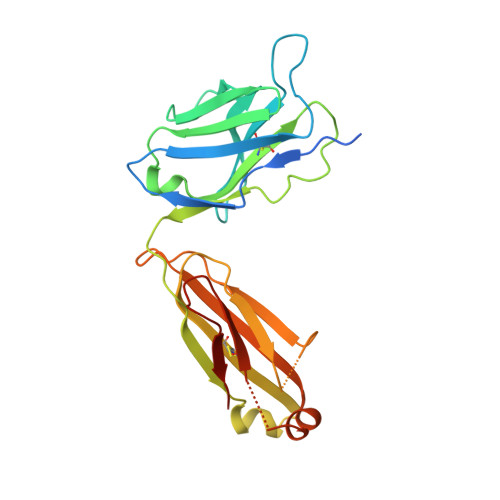
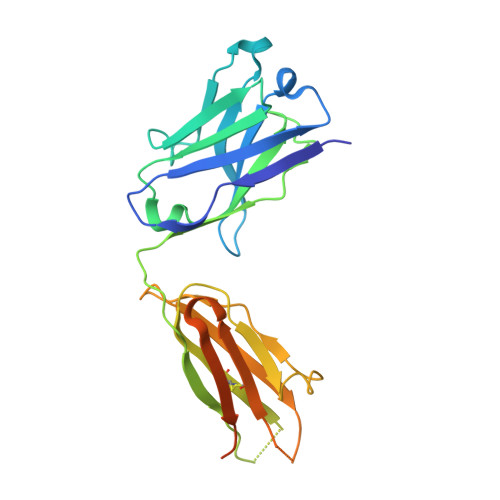
Structure-Function Analysis of the Extended Conformation of a Polyketide Synthase Module.
Li, X., Sevillano, N., La Greca, F., Deis, L., Liu, Y.C., Deller, M.C., Mathews, I.I., Matsui, T., Cane, D.E., Craik, C.S., Khosla, C.(2018) J Am Chem Soc 140: 6518-6521
- PubMed: 29762030
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b02100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6C9U - PubMed Abstract:
Catalytic modules of assembly-line polyketide synthases (PKSs) have previously been observed in two very different conformations-an "extended" architecture and an "arch-shaped" architecture-although the catalytic relevance of neither has been directly established. By the use of a fully human naïve antigen-binding fragment (F ab ) library, a high-affinity antibody was identified that bound to the extended conformation of a PKS module, as verified by X-ray crystallography and tandem size-exclusion chromatography-small-angle X-ray scattering (SEC-SAXS). Kinetic analysis proved that this antibody-stabilized module conformation was fully competent for catalysis of intermodular polyketide chain translocation as well as intramodular polyketide chain elongation and functional group modification of a growing polyketide chain. Thus, the extended conformation of a PKS module is fully competent for all of its essential catalytic functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry , University of California San Francisco , San Francisco , California 94158 , United States.