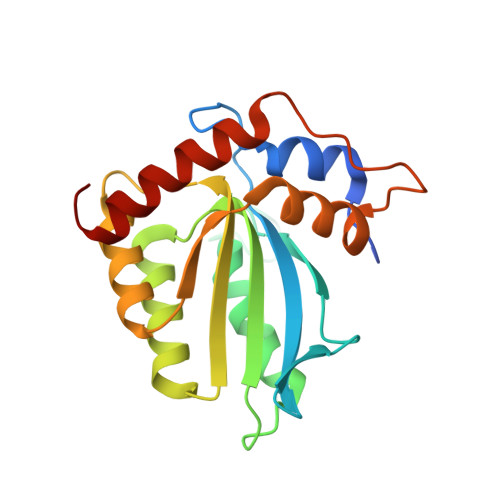
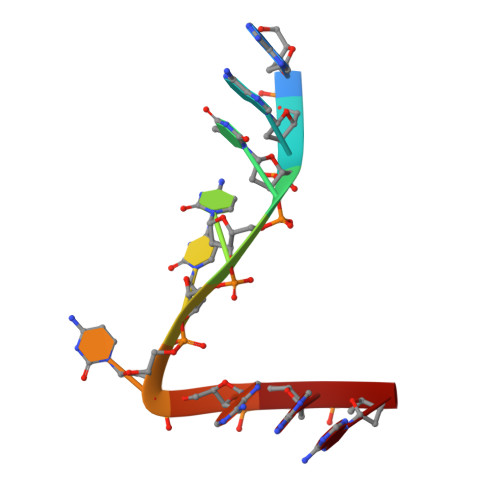
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 restriction factor APOBEC3G in complex with ssDNA.
Maiti, A., Myint, W., Kanai, T., Delviks-Frankenberry, K., Sierra Rodriguez, C., Pathak, V.K., Schiffer, C.A., Matsuo, H.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 2460-2460
- PubMed: 29941968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04872-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BUX - PubMed Abstract:
The human APOBEC3G protein is a cytidine deaminase that generates cytidine to deoxy-uridine mutations in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), and capable of restricting replication of HIV-1 by generating mutations in viral genome. The mechanism by which APOBEC3G specifically deaminates 5'-CC motifs has remained elusive since structural studies have been hampered due to apparently weak ssDNA binding of the catalytic domain of APOBEC3G. We overcame the problem by generating a highly active variant with higher ssDNA affinity. Here, we present the crystal structure of this variant complexed with a ssDNA substrate at 1.86 Å resolution. This structure reveals atomic-level interactions by which APOBEC3G recognizes a functionally-relevant 5'-TCCCA sequence. This complex also reveals a key role of W211 in substrate recognition, implicating a similar recognition in activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) with a conserved tryptophan.
Organizational Affiliation:
Basic Science Program, Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc., Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, Frederick, MD, 21702, USA.