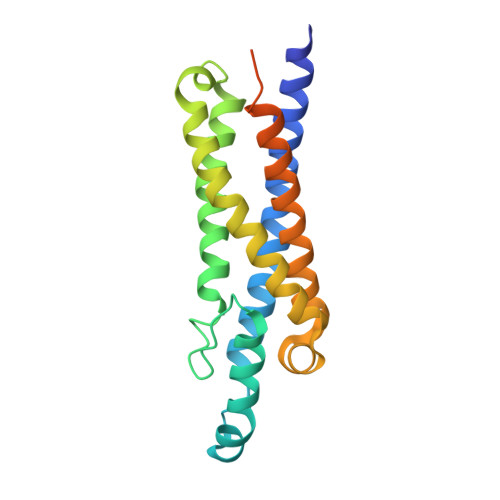
Structure and function of LCI1: a plasma membrane CO 2 channel in the Chlamydomonas CO 2 concentrating mechanism.
Kono, A., Chou, T.H., Radhakrishnan, A., Bolla, J.R., Sankar, K., Shome, S., Su, C.C., Jernigan, R.L., Robinson, C.V., Yu, E.W., Spalding, M.H.(2020) Plant J 102: 1107-1126
- PubMed: 32168387
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14745
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BHP - PubMed Abstract:
Microalgae and cyanobacteria contribute roughly half of the global photosynthetic carbon assimilation. Faced with limited access to CO 2 in aquatic environments, which can vary daily or hourly, these microorganisms have evolved use of an efficient CO 2 concentrating mechanism (CCM) to accumulate high internal concentrations of inorganic carbon (C i ) to maintain photosynthetic performance. For eukaryotic algae, a combination of molecular, genetic and physiological studies using the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, have revealed the function and molecular characteristics of many CCM components, including active C i uptake systems. Fundamental to eukaryotic C i uptake systems are C i transporters/channels located in membranes of various cell compartments, which together facilitate the movement of C i from the environment into the chloroplast, where primary CO 2 assimilation occurs. Two putative plasma membrane C i transporters, HLA3 and LCI1, are reportedly involved in active C i uptake. Based on previous studies, HLA3 clearly plays a meaningful role in HCO 3 - transport, but the function of LCI1 has not yet been thoroughly investigated so remains somewhat obscure. Here we report a crystal structure of the full-length LCI1 membrane protein to reveal LCI1 structural characteristics, as well as in vivo physiological studies in an LCI1 loss-of-function mutant to reveal the C i species preference for LCI1. Together, these new studies demonstrate LCI1 plays an important role in active CO 2 uptake and that LCI1 likely functions as a plasma membrane CO 2 channel, possibly a gated channel.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Genetics, Development, and Cell Biology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, 50011, USA.