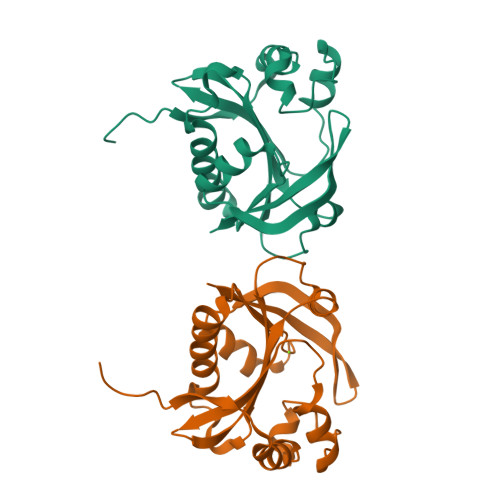
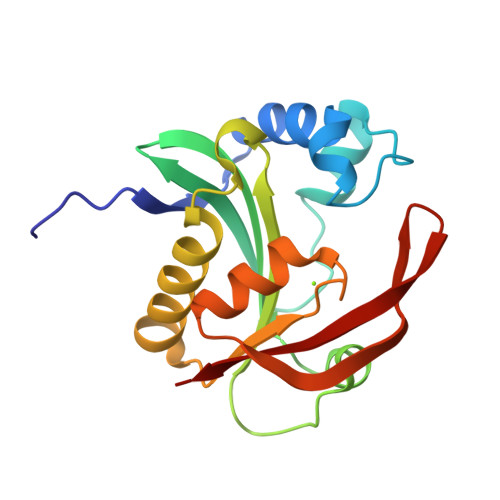
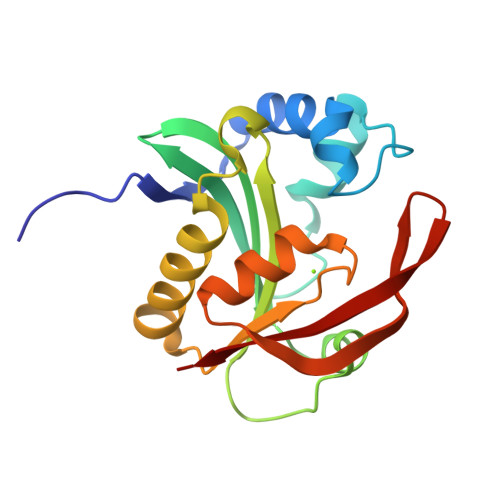
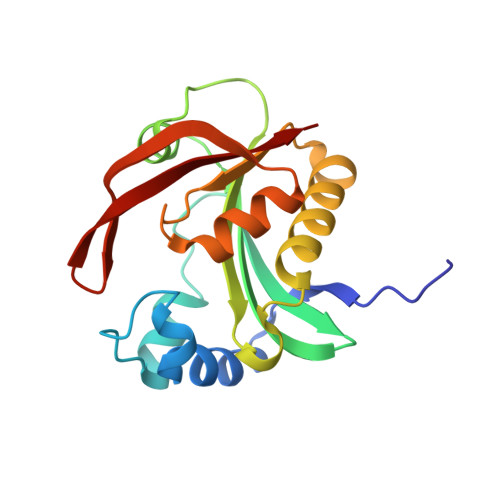
Aminoglycoside resistance profile and structural architecture of the aminoglycoside acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Im.
Smith, C.A., Bhattacharya, M., Toth, M., Stewart, N.K., Vakulenko, S.B.(2017) Microb Cell 4: 402-410
- PubMed: 29234669
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2017.12.602
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BFF, 6BFH - PubMed Abstract:
Aminoglycoside 6'-acetyltransferase-Im (AAC(6')-Im) is the closest monofunctional homolog of the AAC(6')-Ie acetyltransferase of the bifunctional enzyme AAC(6')-Ie/APH(2")-Ia. The AAC(6')-Im acetyltransferase confers 4- to 64-fold higher MICs to 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides and the 4,5-disubstituted aminoglycoside neomycin than AAC(6')-Ie, yet unlike AAC(6')-Ie, the AAC(6')-Im enzyme does not confer resistance to the atypical aminoglycoside fortimicin. The structure of the kanamycin A complex of AAC(6')-Im shows that the substrate binds in a shallow positively-charged pocket, with the N6' amino group positioned appropriately for an efficient nucleophilic attack on an acetyl-CoA cofactor. The AAC(6')-Ie enzyme binds kanamycin A in a sufficiently different manner to position the N6' group less efficiently, thereby reducing the activity of this enzyme towards the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides. Conversely, docking studies with fortimicin in both acetyltransferases suggest that the atypical aminoglycoside might bind less productively in AAC(6')-Im, thus explaining the lack of resistance to this molecule.
Organizational Affiliation:
Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA.