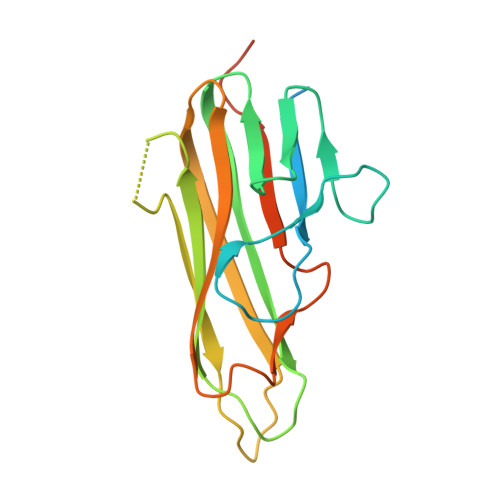
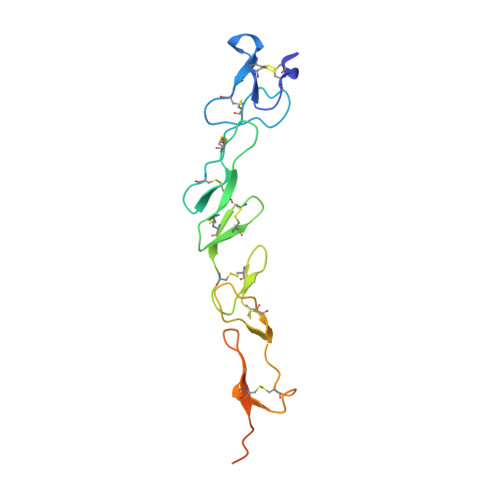
Limited Cross-Linking of 4-1BB by 4-1BB Ligand and the Agonist Monoclonal Antibody Utomilumab.
Li, Y., Tan, S., Zhang, C., Chai, Y., He, M., Zhang, C.W., Wang, Q., Tong, Z., Liu, K., Lei, Y., Liu, W.J., Liu, Y., Tian, Z., Cao, X., Yan, J., Qi, J., Tien, P., Gao, S., Gao, G.F.(2018) Cell Rep 25: 909-920.e4
- PubMed: 30355497
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.073
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6A3V, 6A3W - PubMed Abstract:
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the co-stimulatory molecule 4-1BB are of interest for tumor immunotherapy. We determined the complex structures of human 4-1BB with 4-1BB ligand (4-1BBL) or utomilumab to elucidate the structural basis of 4-1BB activation. The 4-1BB/4-1BBL complex displays a typical TNF/TNFR family binding mode. The structure of utomilumab/4-1BB complex shows that utomilumab binds to dimeric 4-1BB with a distinct but partially overlapping binding area with 4-1BBL. Competitive binding analysis demonstrates that utomilumab blocks the 4-1BB/4-1BBL interaction, indicating the interruption of ligand-mediated signaling. The binding profiles of 4-1BBL and utomilumab to monomeric or dimeric 4-1BB indicate limited cross-linking of 4-1BB molecules. These findings provide mechanistic insight into the binding of 4-1BB with its ligand and its agonist mAb, which may facilitate the future development of anti-4-1BB biologics for tumor immunotherapy.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.