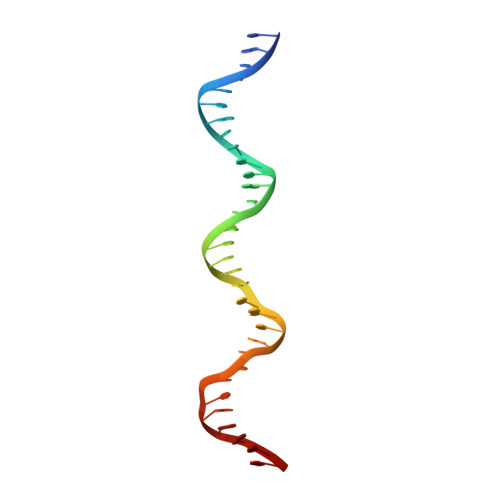
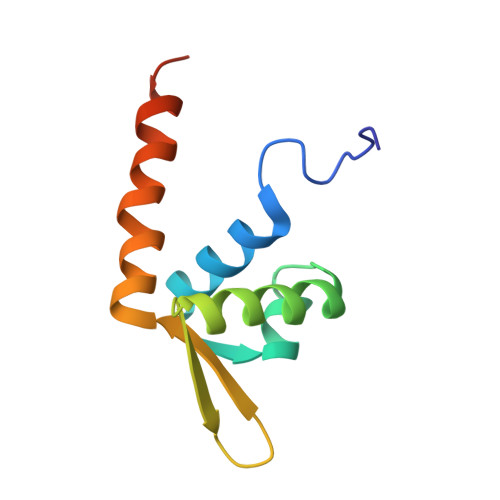
Structures of archaeal DNA segregation machinery reveal bacterial and eukaryotic linkages.
Schumacher, M.A., Tonthat, N.K., Lee, J., Rodriguez-Castaneda, F.A., Chinnam, N.B., Kalliomaa-Sanford, A.K., Ng, I.W., Barge, M.T., Shaw, P.L., Barilla, D.(2015) Science 349: 1120-1124
- PubMed: 26339031
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa9046
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4RS7, 4RS8, 5K5A, 5K5D, 5K5O, 5K5Q, 5K5R, 5K5Z - PubMed Abstract:
Although recent studies have provided a wealth of information about archaeal biology, nothing is known about the molecular basis of DNA segregation in these organisms. Here, we unveil the machinery and assembly mechanism of the archaeal Sulfolobus pNOB8 partition system. This system uses three proteins: ParA; an atypical ParB adaptor; and a centromere-binding component, AspA. AspA utilizes a spreading mechanism to create a DNA superhelix onto which ParB assembles. This supercomplex links to the ParA motor, which contains a bacteria-like Walker motif. The C domain of ParB harbors structural similarity to CenpA, which dictates eukaryotic segregation. Thus, this archaeal system combines bacteria-like and eukarya-like components, which suggests the possible conservation of DNA segregation principles across the three domains of life.
- Department of Biochemistry, Duke University School of Medicine, 243 Nanaline H. Duke, Box 3711, Durham, NC 27710, USA. maria.schumacher@duke.edu daniela.barilla@york.ac.uk.
Organizational Affiliation: