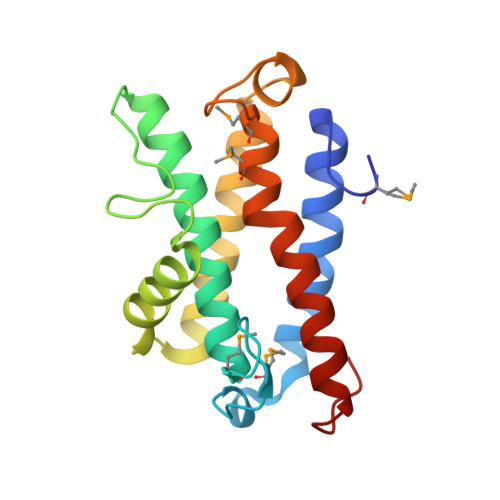
Structures of the DfsB Protein Family Suggest a Cationic, Helical Sibling Lethal Factor Peptide.
Taylor, J.D., Taylor, G., Hare, S.A., Matthews, S.J.(2016) J Mol Biology 428: 554-560
- PubMed: 26804569
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.01.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CIV, 5COF, 5COG, 5COM, 5CQV - PubMed Abstract:
Bacteria have developed a variety of mechanisms for surviving harsh environmental conditions, nutrient stress and overpopulation. Paenibacillus dendritiformis produces a lethal protein (Slf) that is able to induce cell death in neighbouring colonies and a phenotypic switch in more distant ones. Slf is derived from the secreted precursor protein, DfsB, after proteolytic processing. Here, we present new crystal structures of DfsB homologues from a variety of bacterial species and a surprising version present in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adopting a four-helix bundle decorated with a further three short helices within intervening loops, DfsB belongs to a non-enzymatic class of the DinB fold. The structure suggests that the biologically active Slf fragment may possess a C-terminal helix rich in basic and aromatic residues that suggest a functional mechanism akin to that for cationic antimicrobial peptides.
- Department of Life Sciences, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: