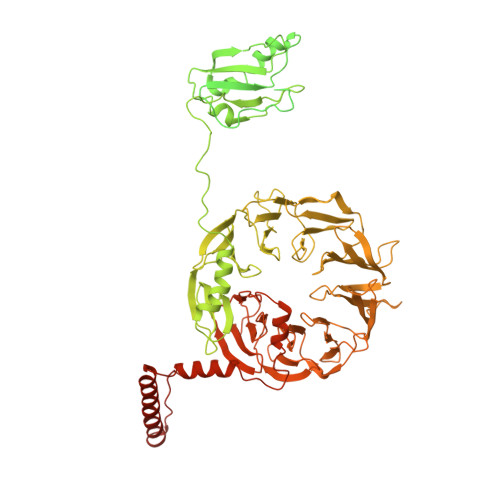
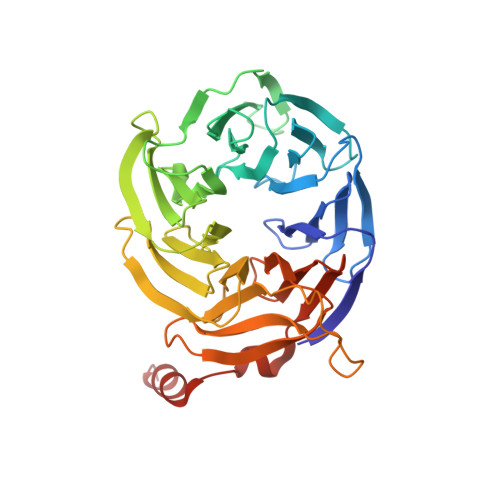
Structure of Mammalian Eif3 in the Context of the 43S Preinitiation Complex.
Des-Georges, A., Dhote, V., Kuhn, L., Hellen, C.U.T., Pestova, T.V., Frank, J., Hashem, Y.(2015) Nature 525: 491
- PubMed: 26344199
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14891
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5A5T, 5A5U - PubMed Abstract:
During eukaryotic translation initiation, 43S complexes, comprising a 40S ribosomal subunit, initiator transfer RNA and initiation factors (eIF) 2, 3, 1 and 1A, attach to the 5'-terminal region of messenger RNA and scan along it to the initiation codon. Scanning on structured mRNAs also requires the DExH-box protein DHX29. Mammalian eIF3 contains 13 subunits and participates in nearly all steps of translation initiation. Eight subunits having PCI (proteasome, COP9 signalosome, eIF3) or MPN (Mpr1, Pad1, amino-terminal) domains constitute the structural core of eIF3, to which five peripheral subunits are flexibly linked. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of eIF3 in the context of the DHX29-bound 43S complex, showing the PCI/MPN core at ∼6 Å resolution. It reveals the organization of the individual subunits and their interactions with components of the 43S complex. We were able to build near-complete polyalanine-level models of the eIF3 PCI/MPN core and of two peripheral subunits. The implications for understanding mRNA ribosomal attachment and scanning are discussed.
- HHMI, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, New York 10032, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: