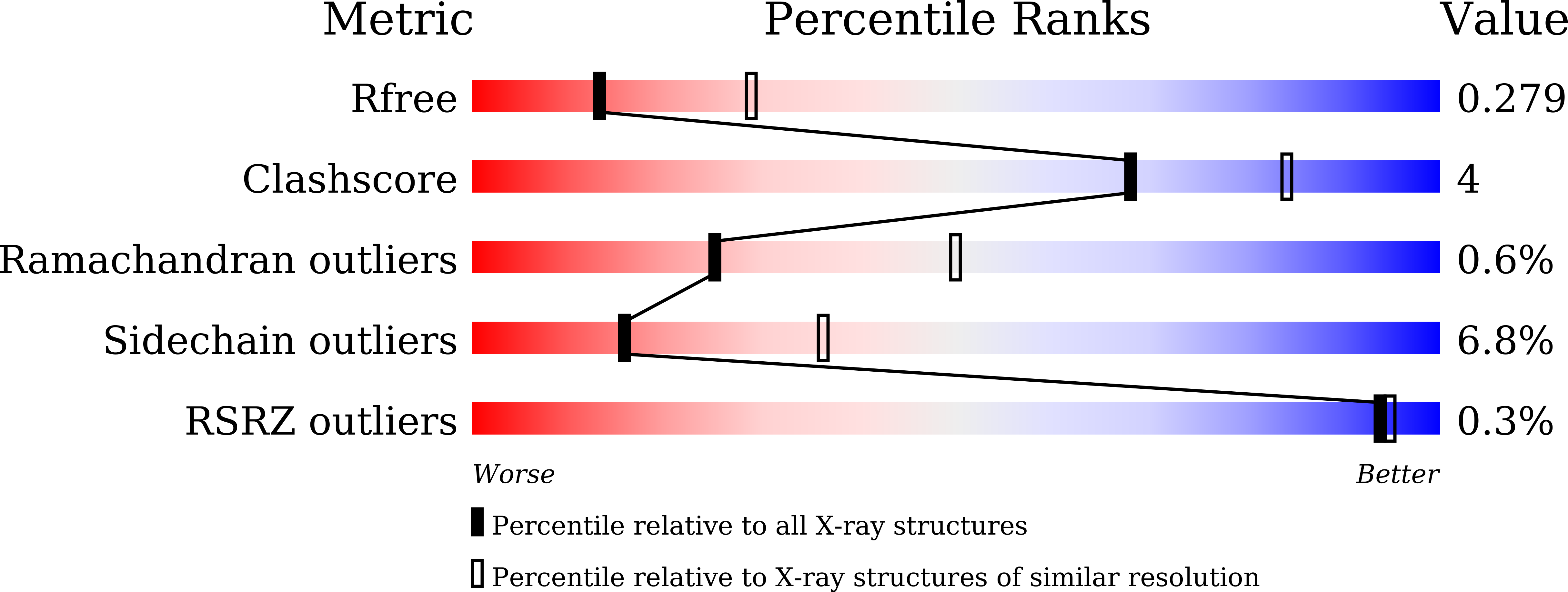
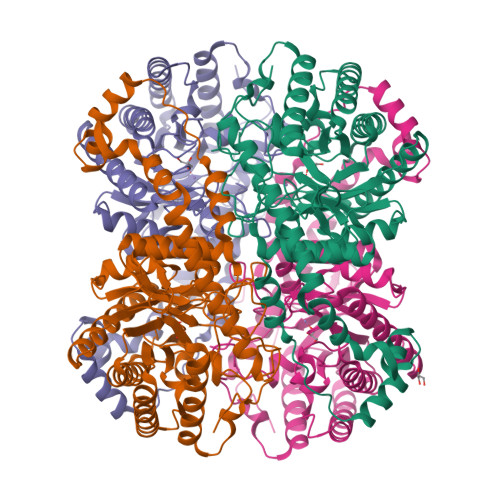
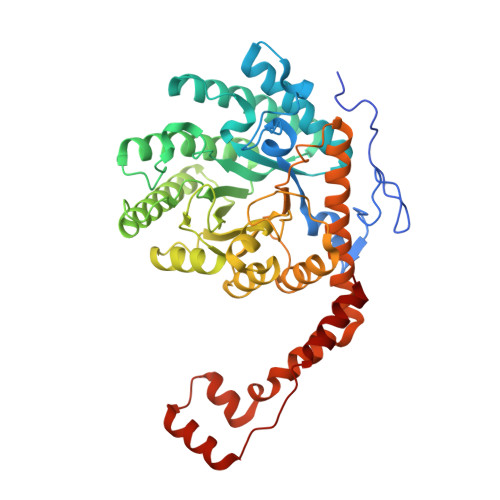
Crystal Structure and Biochemical Characterization of Xylose Isomerase fromPiromycessp. E2.
Son, H., Lee, S.M., Kim, K.J.(2018) J Microbiol Biotechnol 28: 571-578
- PubMed: 29385668
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1711.11026
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YN3 - PubMed Abstract:
Biofuel production using lignocellulosic biomass is gaining attention because it can be substituted for fossil fuels without competing with edible resources. However, because Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not have a D -xylose metabolic pathway, oxidoreductase or isomerase pathways must be introduced to utilize D -xylose from lignocellulosic biomass in S. cerevisiae . To elucidate the biochemical properties of xylose isomerase (XI) from Piromyces sp. E2 ( Ps XI), we determine its crystal structure in complex with substrate mimic glycerol. An amino acid sequence comparison with other reported XIs and the relative activity measurements using five kinds of divalent metal ions confirmed that Ps XI belongs to class II XI. Moreover kinetic analysis of Ps XI was also performed using Mn²⁺, the preferred divalent metal ion for Ps XI. In addition, the substrate-binding mode of Ps XI could be predicted with the substrate mimic glycerol bound to the active site. These studies may provide structural information to enhance D -xylose utilization for biofuel production.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, KNU Creative BioResearch Group, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Republic of Korea.