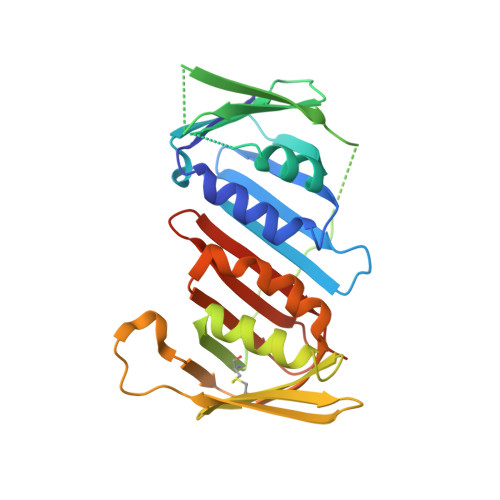
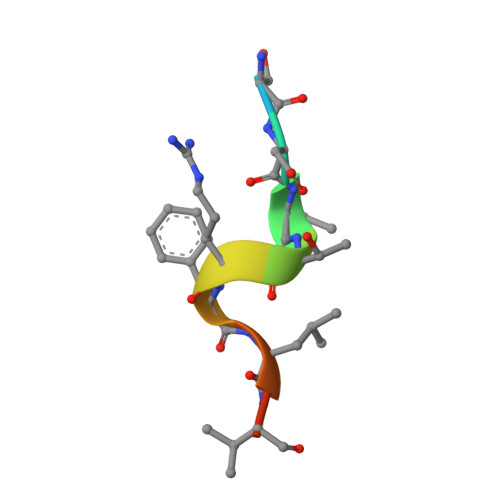
Structure of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) bound to an APIM peptide reveals the universality of PCNA interaction.
Hara, K., Uchida, M., Tagata, R., Yokoyama, H., Ishikawa, Y., Hishiki, A., Hashimoto, H.(2018) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 74: 214-221
- PubMed: 29633969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X18003242
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YD8 - PubMed Abstract:
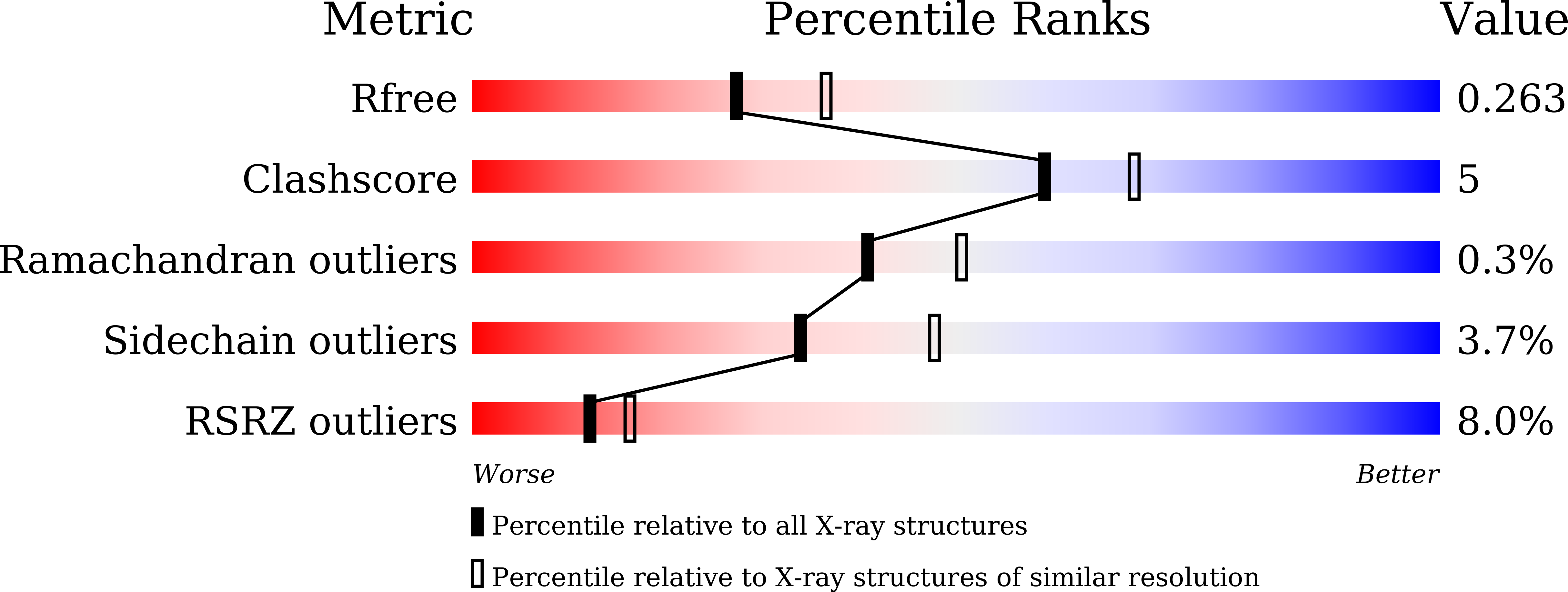
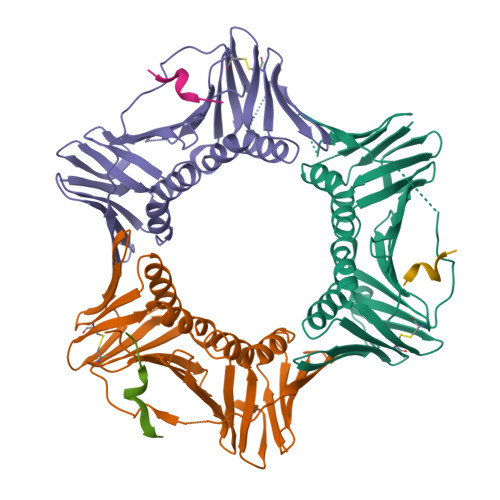
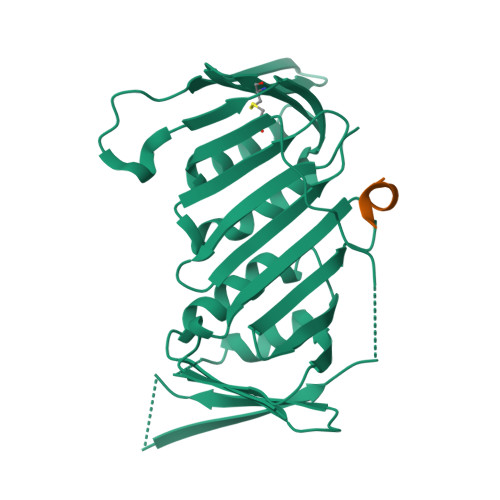
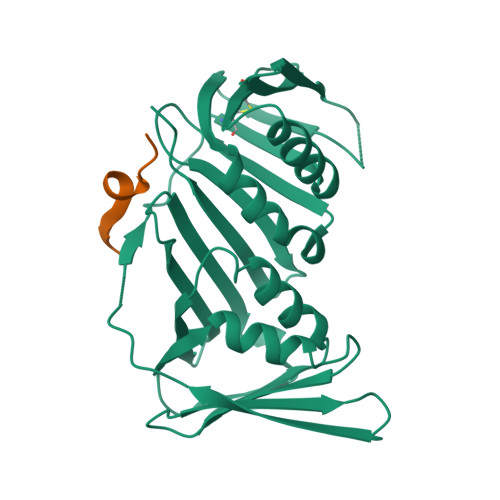
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) provides a molecular platform for numerous protein-protein interactions in DNA metabolism. A large number of proteins associated with PCNA have a well characterized sequence termed the PCNA-interacting protein box motif (PIPM). Another PCNA-interacting sequence termed the AlkB homologue 2 PCNA-interacting motif (APIM), comprising the five consensus residues (K/R)-(F/Y/W)-(L/I/V/A)-(L/I/V/A)-(K/R), has also been identified in various proteins. In contrast to that with PIPM, the PCNA-APIM interaction is less well understood. Here, the crystal structure of PCNA bound to a peptide carrying an APIM consensus sequence, RFLVK, was determined and structure-based interaction analysis was performed. The APIM peptide binds to the PIPM-binding pocket on PCNA in a similar way to PIPM. The phenylalanine and leucine residues within the APIM consensus sequence and a hydrophobic residue that precedes the APIM consensus sequence are crucially involved in interactions with the hydrophobic pocket of PCNA. This interaction is essential for overall binding. These results provide a structural basis for regulation of the PCNA interaction and might aid in the development of specific inhibitors of this interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Shizuoka, 52-1 Yada, Suruga-ku, Shizuoka, Shizuoka 422-8002, Japan.