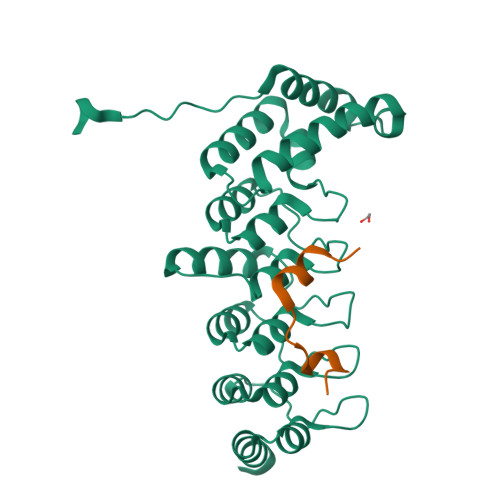
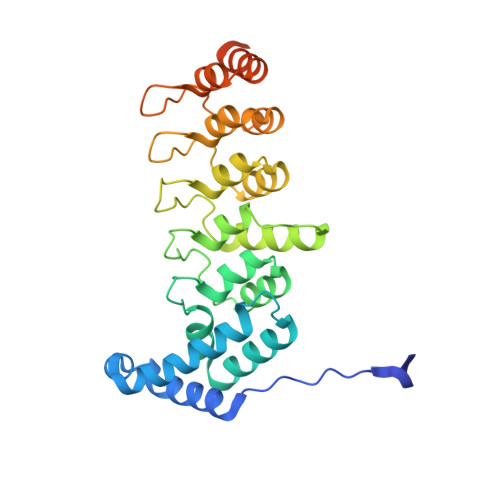
Structural analyses of key features in the KANK1/KIF21A complex yield mechanistic insights into the cross-talk between microtubules and the cell cortex.
Weng, Z., Shang, Y., Yao, D., Zhu, J., Zhang, R.(2018) J Biological Chem 293: 215-225
- PubMed: 29158259
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.816017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YBE - PubMed Abstract:
The cross-talk between dynamic microtubules and the cell cortex plays important roles in cell division, polarity, and migration. A critical adaptor that links the plus ends of microtubules with the cell cortex is the KANK N-terminal motif and ankyrin repeat domains 1 (KANK1)/kinesin family member 21A (KIF21A) complex. Genetic defects in these two proteins are associated with various cancers and developmental diseases, such as congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 1. However, the molecular mechanism governing the KANK1/KIF21A interaction and the role of the conserved ankyrin (ANK) repeats in this interaction are still unclear. In this study, we present the crystal structure of the KANK1·KIF21A complex at 2.1 Å resolution. The structure, together with biochemical studies, revealed that a five-helix-bundle-capping domain immediately preceding the ANK repeats of KANK1 forms a structural and functional supramodule with its ANK repeats in binding to an evolutionarily conserved peptide located in the middle of KIF21A. We also show that several missense mutations present in cancer patients are located at the interface of the KANK1·KIF21A complex and destabilize its formation. In conclusion, our study elucidates the molecular basis underlying the KANK1/KIF21A interaction and also provides possible mechanistic explanations for the diseases caused by mutations in KANK1 and KIF21A .
Organizational Affiliation:
National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 333 Haike Road, Shanghai 201203, China; School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, 100 Haike Road, Shanghai 201210, China.