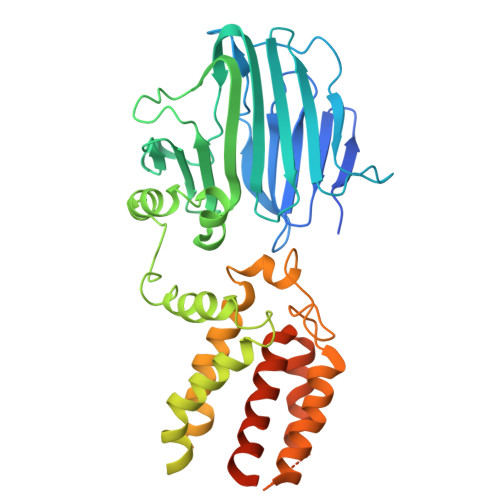
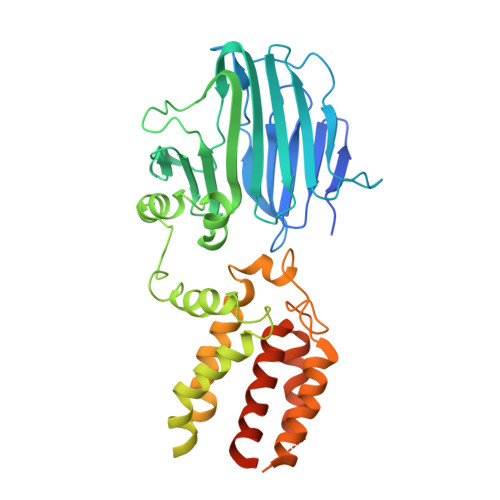
Structure of YidC from Thermotoga maritima and its implications for YidC-mediated membrane protein insertion
Xin, Y., Zhao, Y., Zheng, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, X.C., Tian, C., Huang, Y.(2018) FASEB J 32: 2411-2421
- PubMed: 29295859
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700893RR
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5Y82, 5Y83 - PubMed Abstract:
The evolutionarily conserved YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 family of proteins represents a unique membrane protein family that facilitates the insertion, folding, and assembly of a cohort of α-helical membrane proteins in all kingdoms of life, yet its underlying mechanisms remain elusive. We report the crystal structures of the full-length Thermotoga maritima YidC (TmYidC) and the TmYidC periplasmic domain (TmPD) at a resolution of 3.8 and 2.5 Å, respectively. The crystal structure of TmPD reveals a β-supersandwich fold but with apparently shortened β strands and different connectivity, as compared to the Escherichia coli YidC (EcYidC) periplasmic domain (EcPD). TmYidC in a detergent-solubilized state also adopts a monomeric form and its conserved core domain, which consists of 2 loosely associated α-helical bundles, assemble a fold similar to that of the other YidC homologues, yet distinct from that of the archaeal YidC-like DUF106 protein. Functional analysis using in vivo photo-crosslinking experiments demonstrates that Pf3 coat protein, a Sec-independent YidC substrate, exits to the lipid bilayer laterally via one of the 2 α-helical bundle interfaces: TM3-TM5. Engineered intramolecular disulfide bonds in TmYidC, in combination with complementation assays, suggest that significant rearrangement of the 2 α-helical bundles at the top of the hydrophilic groove is critical for TmYidC function. These experiments provide a more detailed mechanical insight into YidC-mediated membrane protein biogenesis.-Xin, Y., Zhao, Y., Zheng, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, X. C., Tian, C., Huang, Y. Structure of YidC from Thermotoga maritima and its implications for YidC-mediated membrane protein insertion.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory for Physical Science at Microscale, School of Life Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.