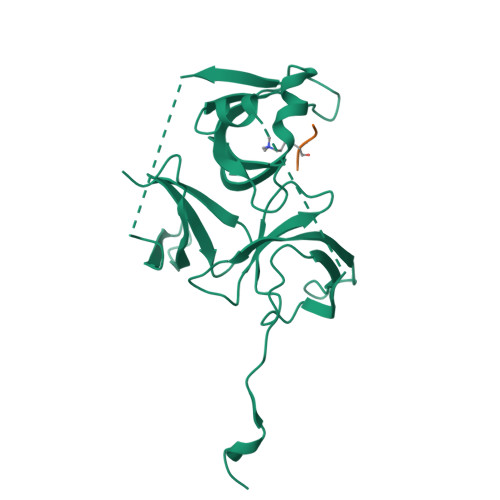
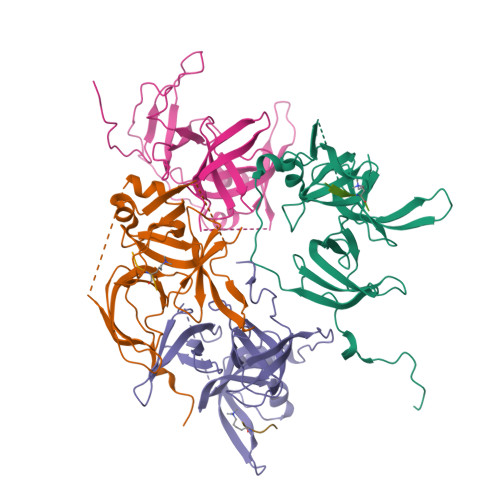
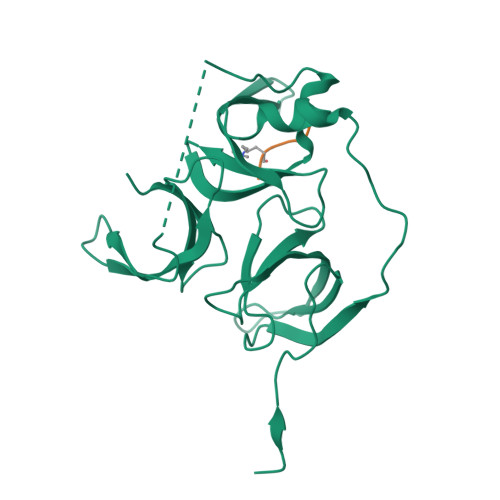
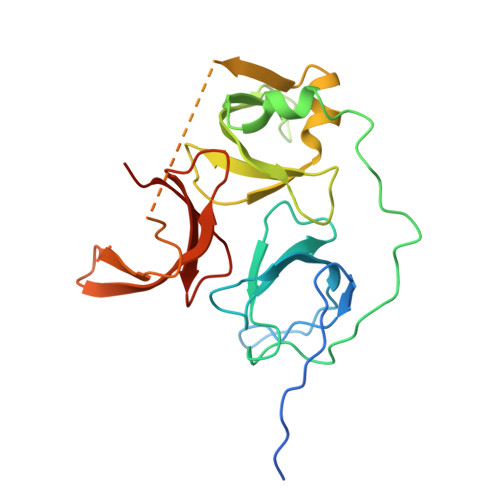
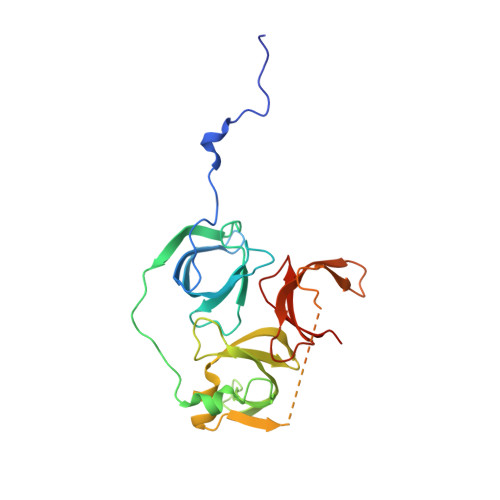
Spindlin-1 recognizes methylations of K20 and R23 of histone H4 tail
Wang, C., Zhan, L., Wu, M., Ma, R., Yao, J., Xiong, Y., Pan, Y., Guan, S., Zhang, X., Zang, J.(2018) FEBS Lett 592: 4098-4110
- PubMed: 30381828
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13281
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5Y5W - PubMed Abstract:
Using methods combining cross-linking, pull-down assays, and stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture with mass spectrometry, we identified that the Tudor domain-containing protein Spindlin-1 recognizes trimethylation of histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me3). The binding affinity of Spindlin-1 to H4K20me3 is weaker than that to H3K4me3, indicating H4K20me3 as a secondary substrate for Spindlin-1. Structural studies of Spindlin-1 in complex with the H4K20me3 peptide indicate that Spindlin-1 attains a distinct binding mode for H4K20me3 recognition. Further biochemical analysis identified that Spindlin-1 also binds methylated R23 of H4, providing new clues for the function of Spindlin-1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Life Sciences and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.