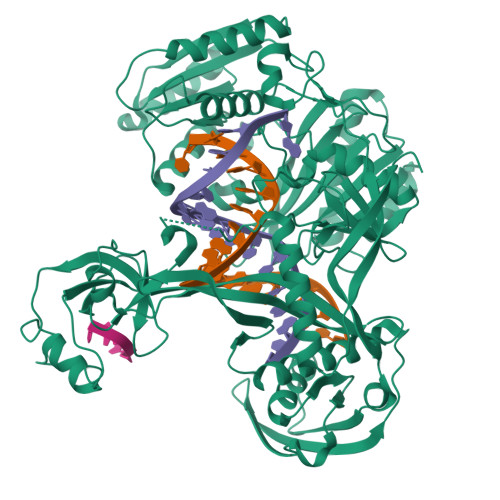
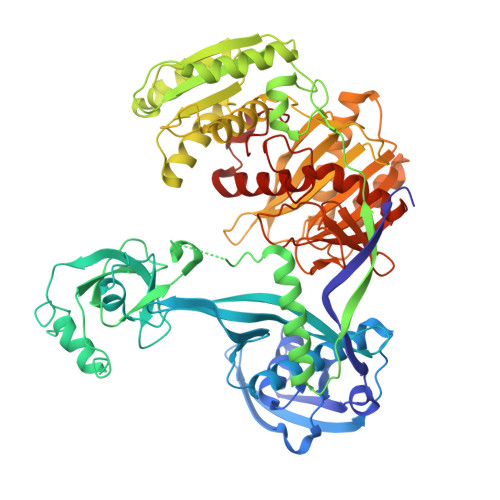
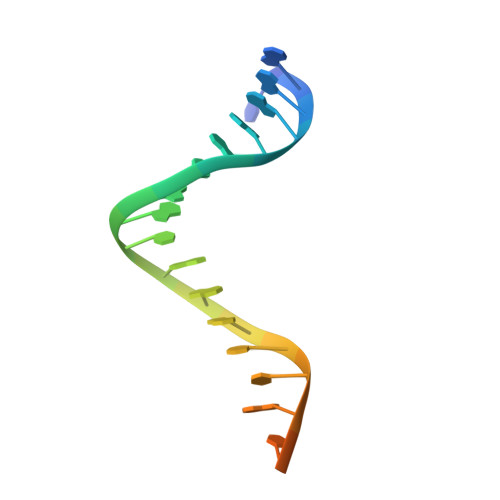
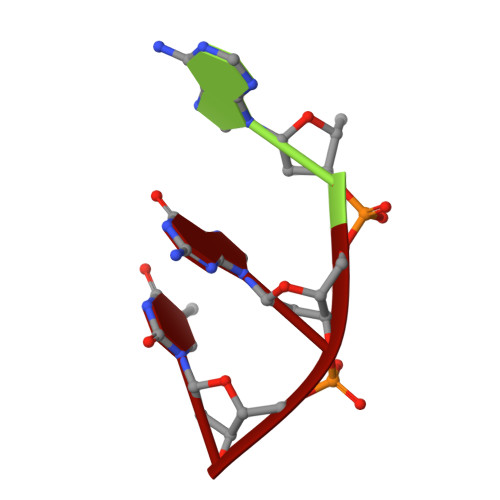
Structure/cleavage-based insights into helical perturbations at bulge sites within T. thermophilus Argonaute silencing complexes.
Sheng, G., Gogakos, T., Wang, J., Zhao, H., Serganov, A., Juranek, S., Tuschl, T., Patel, D.J., Wang, Y.(2017) Nucleic Acids Res 45: 9149-9163
- PubMed: 28911094
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx547
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XOU, 5XOW, 5XP8, 5XPA, 5XPG, 5XQ2 - PubMed Abstract:
We have undertaken a systematic structural study of Thermus thermophilus Argonaute (TtAgo) ternary complexes containing single-base bulges positioned either within the seed segment of the guide or target strands and at the cleavage site. Our studies establish that single-base bulges 7T8, 5A6 and 4A5 on the guide strand are stacked-into the duplex, with conformational changes localized to the bulge site, thereby having minimal impact on the cleavage site. By contrast, single-base bulges 6'U7' and 6'A7' on the target strand are looped-out of the duplex, with the resulting conformational transitions shifting the cleavable phosphate by one step. We observe a stable alignment for the looped-out 6'N7' bulge base, which stacks on the unpaired first base of the guide strand, with the looped-out alignment facilitated by weakened Watson-Crick and reversed non-canonical flanking pairs. These structural studies are complemented by cleavage assays that independently monitor the impact of bulges on TtAgo-mediated cleavage reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of RNA Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.