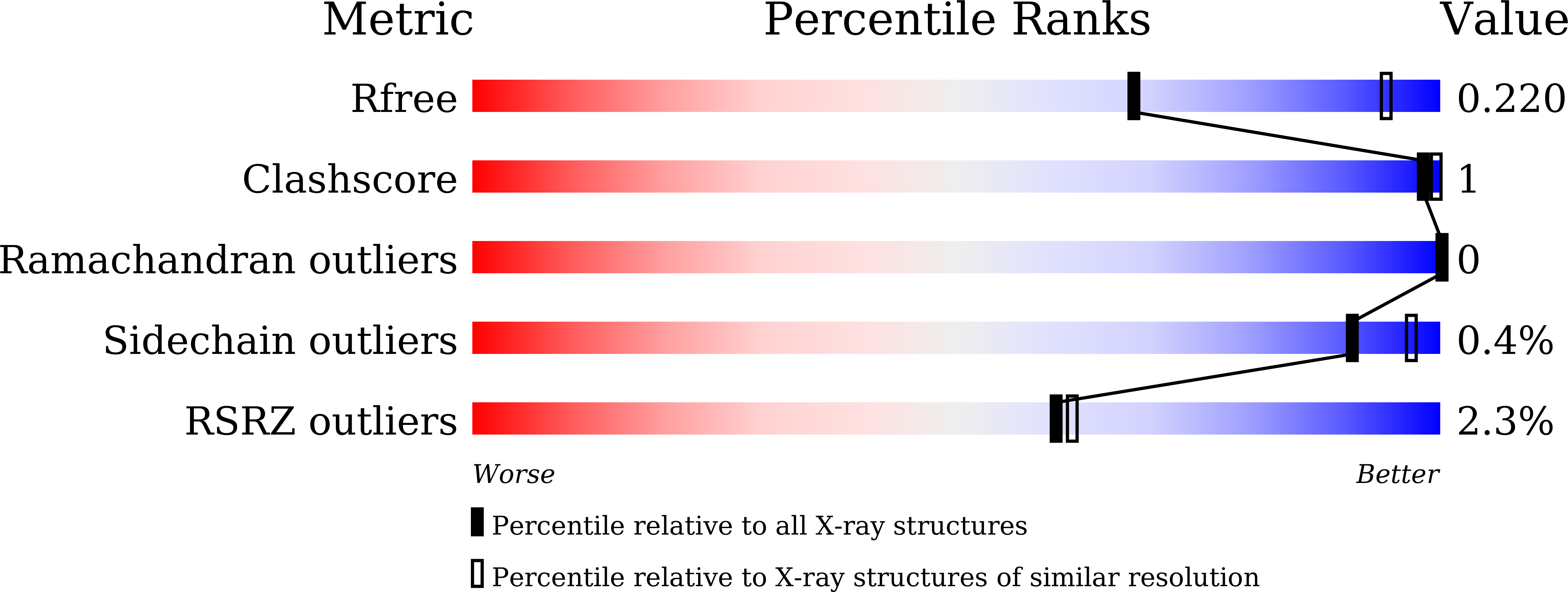
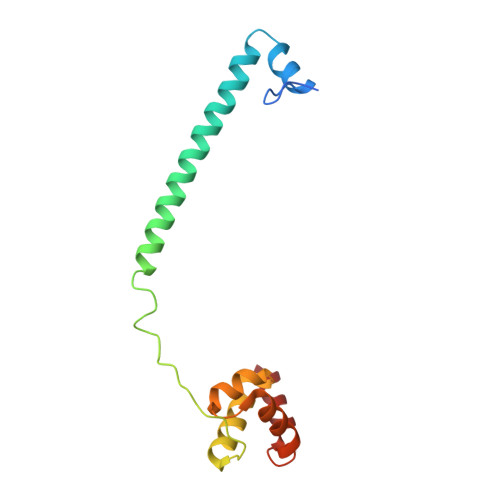
Development and crystallographic evaluation of histone H3 peptide with N-terminal serine substitution as a potent inhibitor of lysine-specific demethylase 1.
Amano, Y., Kikuchi, M., Sato, S., Yokoyama, S., Umehara, T., Umezawa, N., Higuchi, T.(2017) Bioorg Med Chem 25: 2617-2624
- PubMed: 28336409
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.03.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H6Q, 5H6R, 5X60 - PubMed Abstract:
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) is a flavoenzyme demethylase, which removes mono- and dimethyl groups from histone H3 Lys4 (H3K4) or Lys9 (H3K9) in complexes with several nuclear proteins. Since LSD1 is implicated in the tumorigenesis and progression of various cancers, LSD1-specific inhibitors are considered as potential anti-cancer agents. A modified H3 peptide with substitution of Lys4 to Met [H3K4M] is already known to be a potent competitive inhibitor of LSD1. In this study, we synthesized a series of H3K4M peptide derivatives and evaluated their LSD1-inhibitory activities in vitro. We found that substitutions of the N-terminal amino acid with amino acids having a larger side chain were generally not tolerated, but substitution of Ala1 to Ser unexpectedly resulted in more potent inhibitory activity toward LSD1. X-ray crystallographic analysis of H3K4M derivatives bound to the LSD1·CoREST complex revealed the presence of additional hydrogen bonding between the N-terminal Ser residue of the H3 peptide derivative and LSD1. The present structural and biochemical findings will be helpful for obtaining more potent peptidic inhibitors of LSD1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Nagoya City University, 3-1 Tanabe-dori, Mizuho-ku, Nagoya 467-8603, Japan.