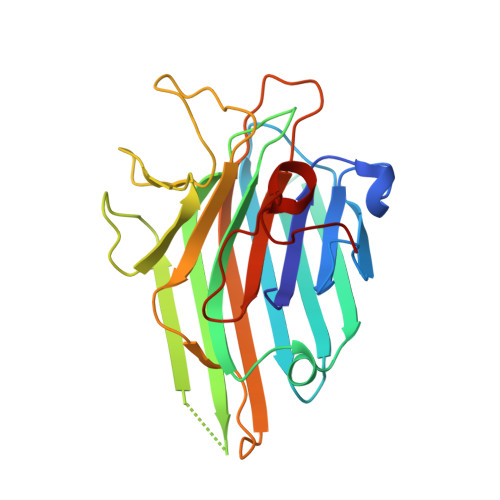
Structural analysis of Dioclea lasiocarpa lectin: A C6 cells apoptosis-inducing protein.
Nascimento, K.S., Santiago, M.Q., Pinto-Junior, V.R., Osterne, V.J.S., Martins, F.W.V., Nascimento, A.P.M., Wolin, I.A.V., Heinrich, I.A., Martins, M.G.Q., Silva, M.T.L., Lossio, C.F., Rocha, C.R.C., Leal, R.B., Cavada, B.S.(2017) Int J Biochem Cell Biol 92: 79-89
- PubMed: 28939357
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.09.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UUY - PubMed Abstract:
Lectins are multidomain proteins that specifically recognize various carbohydrates. The structural characterization of these molecules is crucial in understanding their function and activity in systems and organisms. Most cancer cells exhibit changes in glycosylation patterns, and lectins may be able to recognize these changes. In this work, Dioclea lasiocarpa seed lectin (DLL) was structurally characterized. The lectin presented a high degree of similarity with other lectins isolated from legumes, presenting a jelly roll motif and a metal-binding site stabilizing the carbohydrate-recognition domain. DLL demonstrated differential interactions with carbohydrates, depending on type of glycosidic linkage present in ligands. As observed by the reduction of cell viability in C6 cells, DLL showed strong antiglioma activity by mechanisms involving activation of caspase 3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Universidade Federal do Ceara (UFC), Fortaleza, Ceara, Brazil.