Quenching protein dynamics interferes with HIV capsid maturation.
Wang, M., Quinn, C.M., Perilla, J.R., Zhang, H., Shirra, R., Hou, G., Byeon, I.J., Suiter, C.L., Ablan, S., Urano, E., Nitz, T.J., Aiken, C., Freed, E.O., Zhang, P., Schulten, K., Gronenborn, A.M., Polenova, T.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 1779-1779
- PubMed: 29176596
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01856-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UP4 - PubMed Abstract:
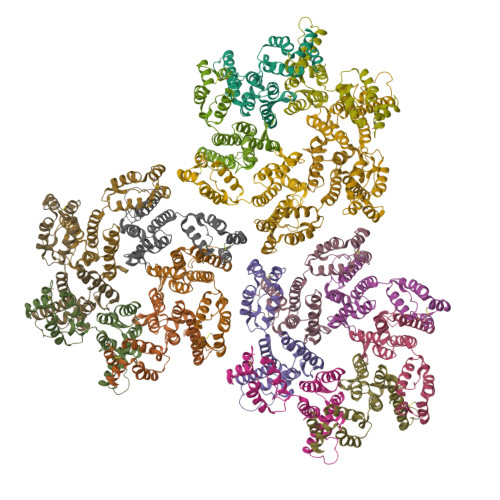
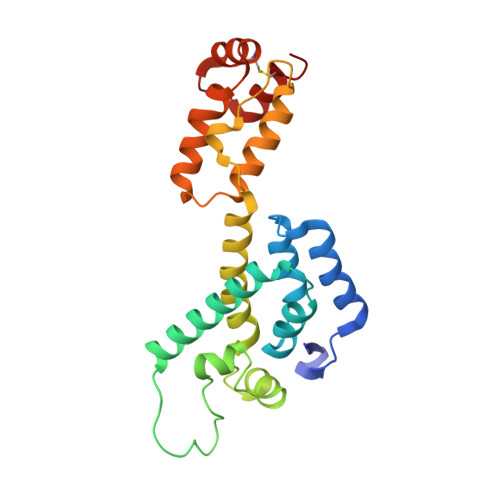
Maturation of HIV-1 particles encompasses a complex morphological transformation of Gag via an orchestrated series of proteolytic cleavage events. A longstanding question concerns the structure of the C-terminal region of CA and the peptide SP1 (CA-SP1), which represents an intermediate during maturation of the HIV-1 virus. By integrating NMR, cryo-EM, and molecular dynamics simulations, we show that in CA-SP1 tubes assembled in vitro, which represent the features of an intermediate assembly state during maturation, the SP1 peptide exists in a dynamic helix-coil equilibrium, and that the addition of the maturation inhibitors Bevirimat and DFH-055 causes stabilization of a helical form of SP1. Moreover, the maturation-arresting SP1 mutation T8I also induces helical structure in SP1 and further global dynamical and conformational changes in CA. Overall, our results show that dynamics of CA and SP1 are critical for orderly HIV-1 maturation and that small molecules can inhibit maturation by perturbing molecular motions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716, USA.