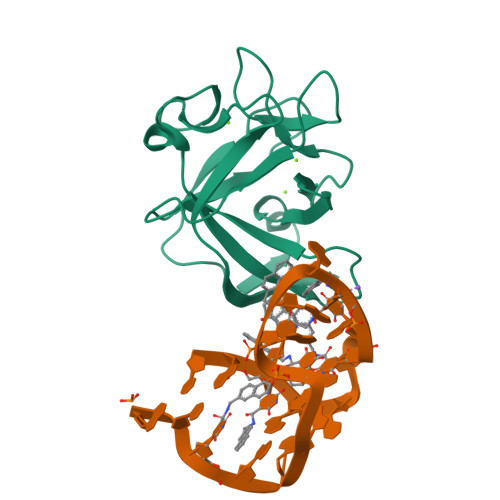
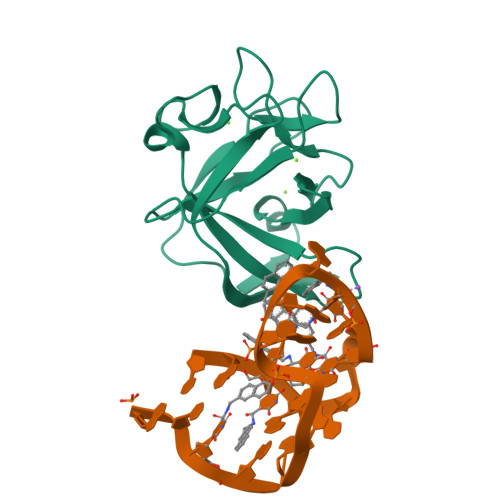
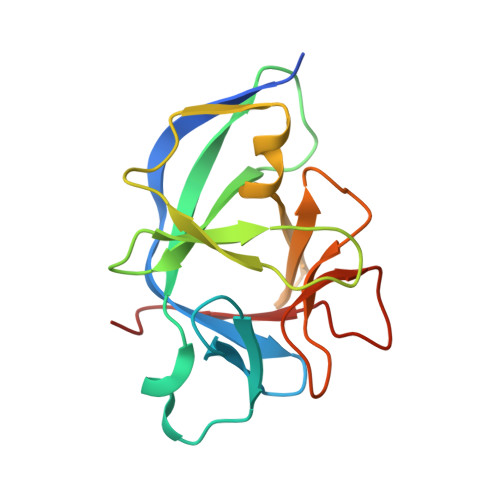
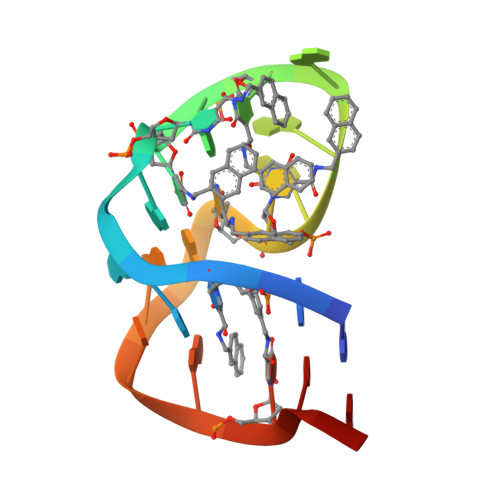
Structural basis for IL-1 alpha recognition by a modified DNA aptamer that specifically inhibits IL-1 alpha signaling.
Ren, X., Gelinas, A.D., von Carlowitz, I., Janjic, N., Pyle, A.M.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 810-810
- PubMed: 28993621
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00864-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UC6 - PubMed Abstract:
IL-1α is an essential cytokine that contributes to inflammatory responses and is implicated in various forms of pathogenesis and cancer. Here we report a naphthyl modified DNA aptamer that specifically binds IL-1α and inhibits its signaling pathway. By solving the crystal structure of the IL-1α/aptamer, we provide a high-resolution structure of this critical cytokine and we reveal its functional interaction interface with high-affinity ligands. The non-helical aptamer, which represents a highly compact nucleic acid structure, contains a wealth of new conformational features, including an unknown form of G-quadruplex. The IL-1α/aptamer interface is composed of unusual polar and hydrophobic elements, along with an elaborate hydrogen bonding network that is mediated by sodium ion. IL-1α uses the same interface to interact with both the aptamer and its cognate receptor IL-1RI, thereby suggesting a novel route to immunomodulatory therapeutics.The cytokine interleukin 1α (IL-1α) plays an important role in inflammatory processes. Here the authors use SELEX to generate a modified DNA aptamer which specifically binds IL-1α, present the structure of the IL-1α/aptamer complex and show that this aptamer inhibits the IL-1α signaling pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, Yale University, 219 Prospect Street, New Haven, CT, 06511, USA.