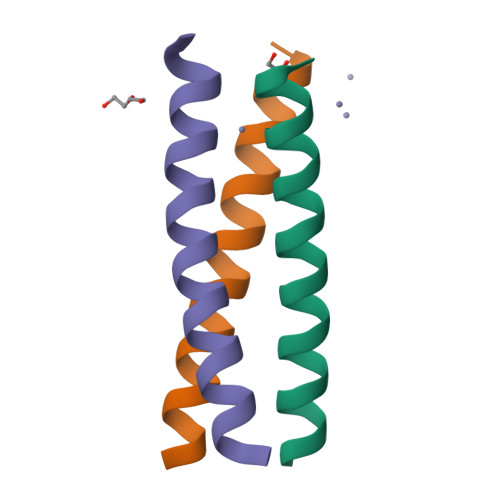
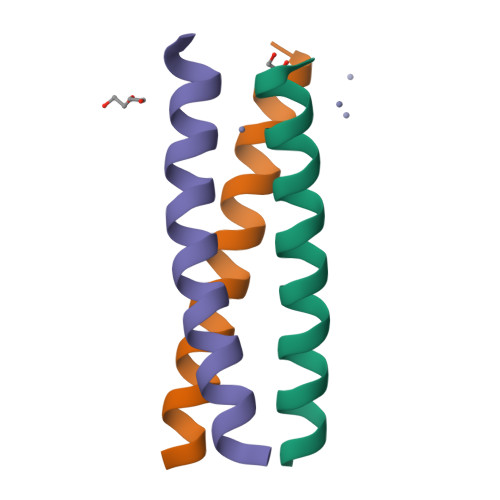
d-Cysteine Ligands Control Metal Geometries within De Novo Designed Three-Stranded Coiled Coils.
Ruckthong, L., Peacock, A.F.A., Pascoe, C.E., Hemmingsen, L., Stuckey, J.A., Pecoraro, V.L.(2017) Chemistry 23: 8232-8243
- PubMed: 28384393
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201700660
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5U9T, 5U9U - PubMed Abstract:
Although metal ion binding to naturally occurring l-amino acid proteins is well documented, understanding the impact of the opposite chirality (d-)amino acids on the structure and stereochemistry of metals is in its infancy. We examine the effect of a d-configuration cysteine within a designed l-amino acid three-stranded coiled coil in order to enforce a precise coordination number on a metal center. The d chirality does not alter the native fold, but the side-chain re-orientation modifies the sterics of the metal binding pocket. l-Cys side chains within the coiled-coil structure have previously been shown to rotate substantially from their preferred positions in the apo structure to create a binding site for a tetra-coordinate metal ion. However, here we show by X-ray crystallography that d-Cys side chains are preorganized within a suitable geometry to bind such a ligand. This is confirmed by comparison of the structure of Zn II Cl(CSL16 D C) 3 2- to the published structure of Zn II (H 2 O)(GRAND-CSL12AL16 L C) 3 - . Moreover, spectroscopic analysis indicates that the Cd II geometry observed by using l-Cys ligands (a mixture of three- and four-coordinate Cd II ) is altered to a single four-coordinate species when d-Cys is present. This work opens a new avenue for the control of the metal site environment in man-made proteins, by simply altering the binding ligand with its mirror-imaged d configuration. Thus, the use of non-coded amino acids in the coordination sphere of a metal promises to be a powerful tool for controlling the properties of future metalloproteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 48109, USA.