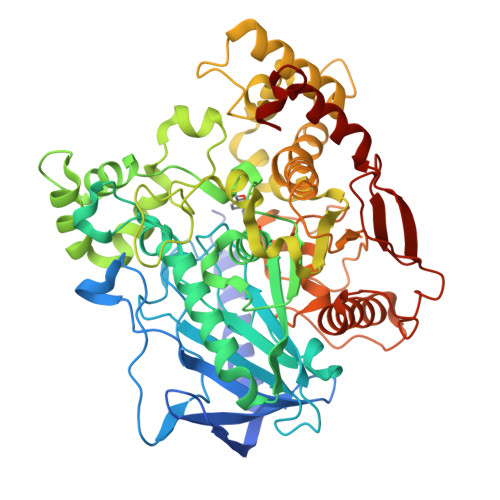
Overcoming insecticide resistance through computational inhibitor design.
Correy, G.J., Zaidman, D., Harmelin, A., Carvalho, S., Mabbitt, P.D., Calaora, V., James, P.J., Kotze, A.C., Jackson, C.J., London, N.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 21012-21021
- PubMed: 31575743
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909130116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TYJ, 5TYK, 5TYL, 5TYM, 5TYN, 5TYO, 5TYP - PubMed Abstract:
Insecticides allow control of agricultural pests and disease vectors and are vital for global food security and health. The evolution of resistance to insecticides, such as organophosphates (OPs), is a serious and growing concern. OP resistance often involves sequestration or hydrolysis of OPs by carboxylesterases. Inhibiting carboxylesterases could, therefore, restore the effectiveness of OPs for which resistance has evolved. Here, we use covalent virtual screening to produce nano-/picomolar boronic acid inhibitors of the carboxylesterase αE7 from the agricultural pest Lucilia cuprina as well as a common Gly137Asp αE7 mutant that confers OP resistance. These inhibitors, with high selectivity against human acetylcholinesterase and low to no toxicity in human cells and in mice, act synergistically with the OPs diazinon and malathion to reduce the amount of OP required to kill L. cuprina by up to 16-fold and abolish resistance. The compounds exhibit broad utility in significantly potentiating another OP, chlorpyrifos, against the common pest, the peach-potato aphid ( Myzus persicae ). These compounds represent a solution to OP resistance as well as to environmental concerns regarding overuse of OPs, allowing significant reduction of use without compromising efficacy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 2601, Australia.